- Chemical Reaction and Equation
The Chemical Reaction and Equation is the first chapter of Science covers the syllabus of class 10 covers the basic idea of chemical Reaction ,it’s kind .
Skeletal Chemical Reaction and equation are usually unbalanced equat but there are few which need not to be balanced as they are already balanced
SKELETON CHEMICAL EQUATION
C s.+ O2 g ———-> CO2g ———————- Cs+ O2g ——–>CO2 g
Zn s + H2SO4 l ——-.> ZnSO4 + H2 g ———-Zn s +H2SO4 ———-> ZnSO4 + H2 g
When two or more substance react with each other the process in which new substances with new properties are formed itis called chemical reaction.
The chemical reaction takes place is in form of change in state, change in colour ,change in temperature and evolution of gas .
REACTANTS of Chemical Reaction and Equation
The substances that takes part in chemical reaction. They are on the left side of reaction
PRODUCTS of Chemical Reaction and Equation
The substances which are formed after the chemical reaction. In form of digestion of food,Respiration ,Rusting of iron, formation of curd.
They are on the right side of reaction.
Znic + Sulphuric acid (reactant) ————–> Znicsulphate + Hydrogen (product)
Zn ( s )+ H2SO4 ( l ) (reactant)————–> ZnSO4 +H2 ( g) (prodqt)
CHEMICAL EQUATION
: A chemical reaction can be represented by chemical equation which involve symbols of the elements /chemical formula of reactant and product with their physical state along with temperature, pressure and use of catalyst if possible should be mentioned
such as Magnesium is burnt in air to form magnesium oxide but before doing so Mg ribbon must be cleaned nicely because it readily react with oxygen to form MgO which do not burn in air.
2 Mg + O2 ———-> 2MgO
This a balanced equation . The balanced equation obeys the law of mass conservation that mass can neither be created nor can be destroyed but transformed in other form
so number of atoms of the elements of reactant must be equal to number of atoms of elements of product so formed as in the above equation two atoms of Mg react with two atoms of oxygen gives two atoms of MgO.
H2 +Cl2 ————> 2HCl
BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 ———> Ba(SO4)3 + 2AlCl
2 Na +2H2O ————–> 2NaOH + H2
A solution of barium chloride when react with sodium sulphate solution it gives insoluble barium sulphate and solution of sodium chloride
Ba Cl2 + Na2(SO4) ————> BaSO4 +2NaCl.
Sodium hydroxide solution (water) react with hydrochloric acid (water) gives sodium chloride and water
NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) ———–>NaCl +H2O
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS and EQUATION:
Ther are various types of chemical reaction
i) COBINATION REACTION and EQUATION: When two or more elements combine to form a single element A+B——>C example Calcium oxide (CaO) react vigorously with water to produce calcium hydroxide (slaked lime ) (Ca (OH)2 )
Cao (s) + H2O ———–> Ca (OH)2 aq
Quick lime ——–> slaked lime this is used in whitewash when slaked lime react with carbon dioxide from air form a thick layer of calcium carbonate gives the shiny look on walls.
Ca (OH)2 (aq)+ CO2 (g)————> CaCO3 (s)+H2 (l).
burning of coal ; C (s) + O2 (g) ——–> CO2 (g)
formation of water : 2H2(g) + O2 ——–> 2H2O (l)
EXOTHERMIC CHEMICAL REACTIONS and EQUATION : The reactions in which heat is released with the formation of products. as burning of natural gas
s exothermic reaction
C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (g) ————>6CO2(aq) + 6 H2O (l) +energy
these carbohydrates broken down to form glucose and this glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of body and produces energy it is the respiration process. The decomposition of vegetable matter into compost is another example .
DECOMPOSITION Chemical Reaction and Equation:
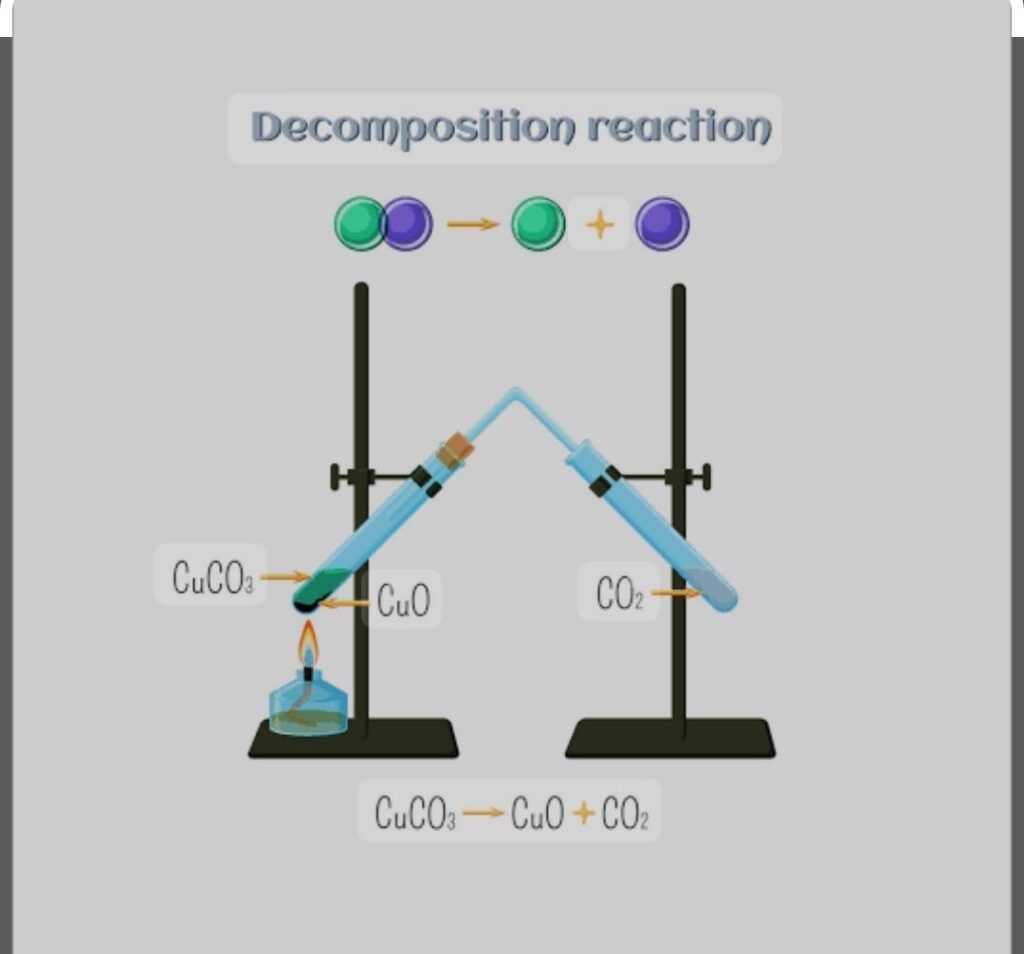
In this kind of reaction single compound is break into two or more compound
2 FeSO4 (s) —- heated ——–> Fe2 O3 (s)+ SO2 (g) + SO3(g)
When ferrous sulphate is heated it gives ferric oxide, Sulphur di oxide and Sulphur tri oxide in form of gases. When calcium carbonate is heated gives calcium oxide and carbon di oxide
CaCO3 (s) ——-heated ———-> CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
when lead nitrate is heated it gives lead oxide and nitrogen di oxide (brown colour gas)
2 Pb (NO3)2(s) ——–heated ——–> 2PbO (s) + 4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
White silver chloride turns into grey in sunlight this is due to decomposition of silver chloride and chlorine by light .2 AgCl —-sunlight ———-> 2Ag (s) + Cl2 (g)
2 AgBr (s) ——-sunlight———–> 2Ag + Br2 (g) this reaction is used in black and white photography .
DISPLACEMENT Chemical Reaction and Equation : When Iron is dipped in copper sulphate the blue colour of copper sulphate fades into white due to the formation of iron sulphate. A+BC–>AC +B
Fe (s) + CuSO4(aq) ————> FeSO4 (s) + Cu (s)
Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) ————> ZnSO4 (s) + Cu (s)
Pb (s) +CuCl2 (aq) ————–> PbCl2 (s) + Cu (s) Znic and lead are more reactive.
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT Chemical Reaction and Equation :
In this reaction the displacement of one element ot the other and vice versa.
AB +CD —-> AD +CB.
In this reaction white substances is obtained ,insoluble in water this is called precipitation and the reaction is the precipitation reaction. When sodium sulphate (aq) is reacted with Barium chloride (aq) it gives the insoluble precipitate of Barium sulphate and sodium chloride solution
Na2SO4 + BaCl2————-> BaSO4 (white ppt ) + 2NaCl
ELCTROLSIS OF WATER :
When acidified water is electroysised with the help of two electrode water molecule breaks into H+ and OH- ion at anode positive charge electrode oxygen is obtained and at negative charge cathode hydrogen gas is produced fig from book NCERT 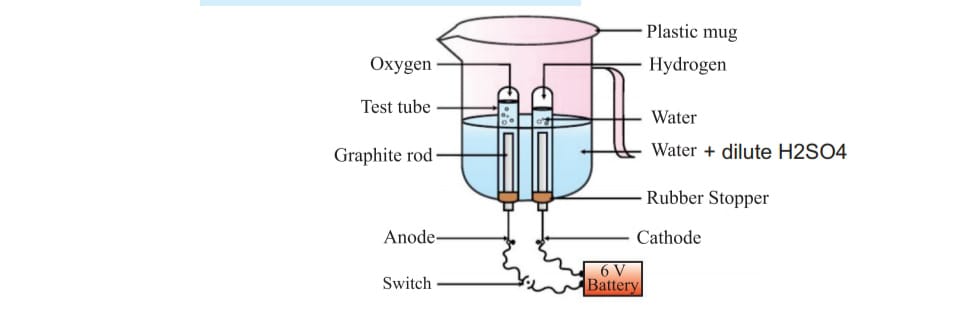
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
When oxygen is added to or hydrogen is removed from or electrons are remove from any substance such substances are said to be oxidised and they help in reduction so they are also called reducing agent .
When Hydrogen is added or oxygen is removed from or electrons are added to any substance it is said to be reduce as it help in oxidation so called oxidising agent
Copper (II) when react with oxygen it becomes black in colour due to oxygen copper is oxidised
2Cu + O2 ——–> 2CuO (BLACK)
CuO +H2 ———> Cu + H2O (BROWN) reduced as oxygen is removed hydrogen is gaining oxygen therefore oxidised.
In this reaction one is oxidise whereas other os rediced so this reaction is called redox reaction.
ZnO + C————-> Zn +CO or
MnO2 +4HCl——–> MnCl2 +2H2O + Cl2
In the above reaction ZnO and MnO2 are reduced to Zn and MnCl2
CORROSION : When a metal is attacked by the substances around it suchas moisture, acids etc it is said to be corrode the process is called corrosion .Brownish powder formed on iron called rusting , black coating on silver due to sulphide and green surface on copper are the example of corrosion.
RANCIDITY : When fats and oil are oxidised they become rancid it’s smell and taste changes for this antioxidant are added to foods containing fats and oil, that is keeping food in airtight containers which slow down the oxidation. Chips manufacturers flush bags of chips with the inert gas such as nitrogen to prevent the chips from getting rancid and oxidised.
Conclusion : Chemical Reaction and Equation
In the chapter Chemical Reaction and Equation types of reactions, its kind with examples , basic idea of oxidation – Reduction reaction ,definition of corrosion ,rancidity are given to cover the whole syllabus to give right path to readers.
Follow us on: Facebook
Read More : Acids Bases and Salts
Read More : Metals and Non Metals