Work and Energy
Work and Energy is the chapter Science covers the basic understanding of the subject that covers the syllabus of class 9

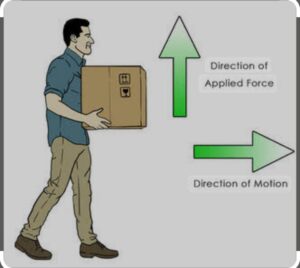
WORK : When the force is applied to the body , it displaces in the direction of force applied than work is said to be done.
The main condition of work done are a) application of force b) displacement in the body
Work done = Force x displacement made
It is a scalar quantity
SI unit of work is Newton – meter or Joule
If greater the force more will be the work done or if more is the displacement more shall be the work done
One Joule is defined as when one newton of force is applied to the body such that it displaces by one meter in the direction of the application of force.
When work is done against the gravity than the amount of work done is equal to the product of weight of body and the vertical distance through which the is lifted
weight of body = mass x acceleration due to gravity =Mg
vertical height to which body is lifted =h
WORK DONE AGANIST GRAVITY = Mgh unit Joule or Newton meter
Work is done when a cyclist is moving/ peddling the cycle or man is lifting a load up ward/ down wards but no work is done when a coolie carrying the load on his head stands stationary or man applied the force on big heavy rock .
Work Done is said to be positive if the displacement and the force is made in same direction example a child pulling the toy
Work Done is said to be negative if the displacement of body is in opposite direction to the force of application example a boy throw a ball on the wall the ball bounces back or a boy kicks the football and it stops after moving some distance due frication
Work Done is said to be zero when force acts at the right angle to the direction of motion of the body example circular motion the moon moves around the earth , the revolves around the sun.
Example :A person lift the luggage of 16kg from the ground to the height of 5meter
work against gravity is Mgh = 16 x10x5 = 800 joule
ENERGY : As we know the sun is the main source of energy and most of the energy is derived from the sun , some from the nucleus of atoms as well as interior of the earth
ENERGY IS DEFINED AS THE CAPACITY OF DOING WORK.
The amount of energy present in body is equal to the amount of work done by the body there are case that in working it may loses /gain the energy
.It is scalar quantity
SI unit is Joule
Form of Energy : Kinetic , Potential, Heat OR sound etc
The Energy possessed by the body due to motion or position of the body is called mechanical energy.
Mechanical Energy = Kinetic Energy + Potential Energy
KINETIC ENERGY : The energy possessed by the body due to motion of the body example as moving of cricket ball , running water , moving bullet etc.

It is directly proportional to the mass of the body and square of the velocity .
Formula of KE : 1/2x mxv²
Kinetic energy of the moving body is equal to the work it can do before coming to rest.
If an object of mass m is moving body with the uniform velocity” u” it displaces by distance s with constant force “F “acts on it in direction of displacement velocity changes to” v” having an acceleration” a”
WORK DONE = Force x displacement
= F x s
= ma x s (f= m.a)
V² -U²= 2 a. s
s =( V² -U²) ÷ 2a
W = m.a.s
W is work done m is mass a is acceleration s is displacement
W= ma. (v²- u²) /2a
===> W= m.( v²-u²)/2
W = 1/2 .m (v²- u²) if u=0 ====> W= 1/2 m. v2
K = 1/2 m. v²
example : If the body with the mass of 15kg moving with the velocity of 4 m/s than
KE = 1/2 x 15×4² = 1/2x15x16= 15 x8 = 120 joule
If the mass of body become double/ half the KE also become double / half .
If the velocity becomes double than KE becomes square time ie 4 times or
if the velocity is made half than KE becomes 1/4 times
POTENTIAL ENERGY : The energy possessed by the body due to position of the body/ change in the shape of the body
Example a) water store in dam
b) wound of sting toy
c) Bent string of bow.
Factors :
Mass of the body , greater the mass more is the potential energy if height remain unchanged,
It also depend s upon the height from the surface of earth if mass is constant .Change in shape greater the stretching/twisting/bending greater the potential energy.
Formula of Potential Energy :
If the mass of the object be m it is raised to the height H from the surface of earth acceleration due to gravity tending downwards is g than the work done in taking the body to height H is equal to force x displacement made
PE = Weight x height
= mg x H
= mgH unit joule .
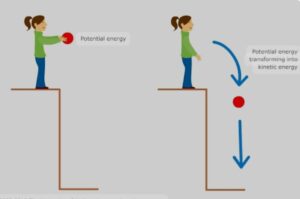
It is to be noted that if weight of body is constant than PE remain same if height is same.
Example :
a) A stone on a certain height has entire potential energy. But when it starts moving downward. PE of stone goes on decreasing as the height goes on decreasing but KE increasing as the velocity increasing as it reaches on the ground the KE is maximum and PE is zero as total PE changes to KE
b) In hydroelectric power the water stored in dam is transformed into KE to produce into electricity .
c) In thermal power the chemical energy of coal is changed into heat in energy which further into KE and Electrical energy.
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY :
Energy can neither be created nor can be destroyed total energy of the system remain conserved .
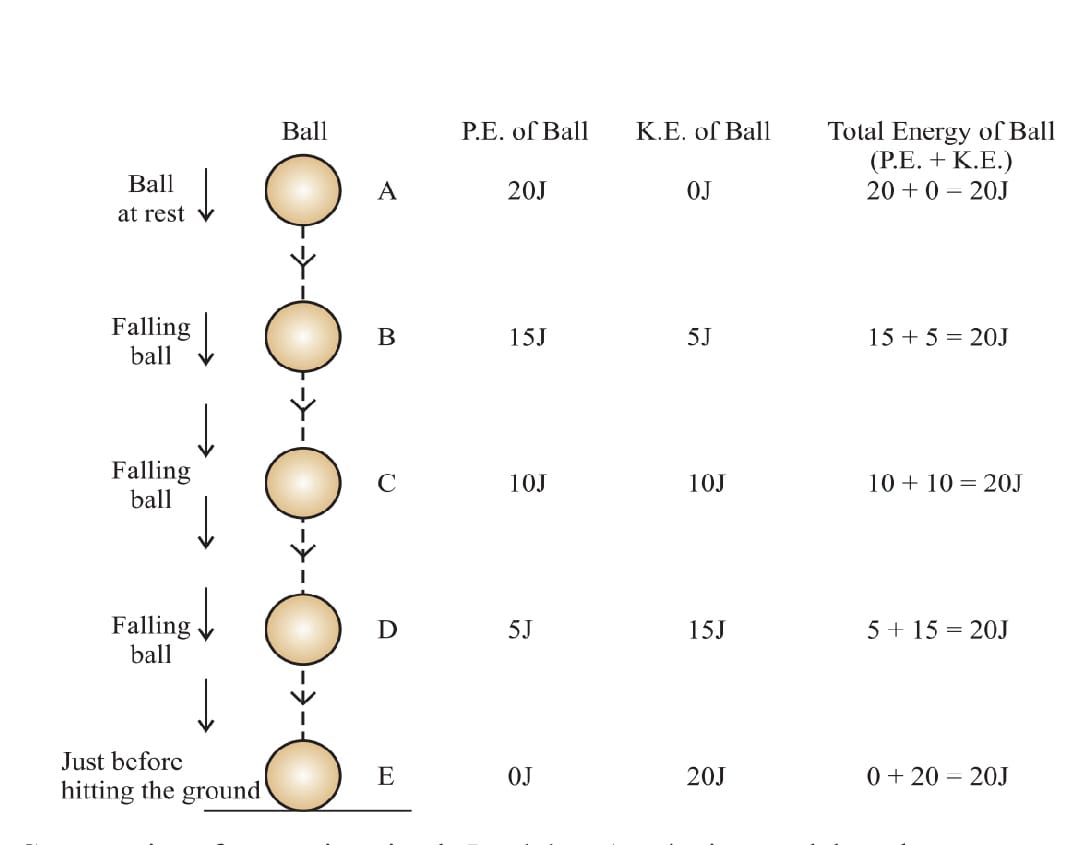
CONSEVATION OF ENERGY DURING FREE FALL OF BODY :
A ball of mass m at the height h has PE is mgh. As a ball falls downwards , the height h decreases so PE changes to KE . In this case PE decreases continuously whereas KE increases .Total energy remain conserved.
Total Energy = Potential Energy + Kinetic Energy ==> TE = PE+KE
1/2 mv²+ mgh = Constant
The conservation of energy ins the pendulum shows the example the a simple pendulum A swing shows the conservation of energy > A swinging of simple pendulum which consist of pith ball / bob which is free to swing back and forth when displaced In this energy is continuously transformed from PE to KE and vice versa . The total energy remain conserved.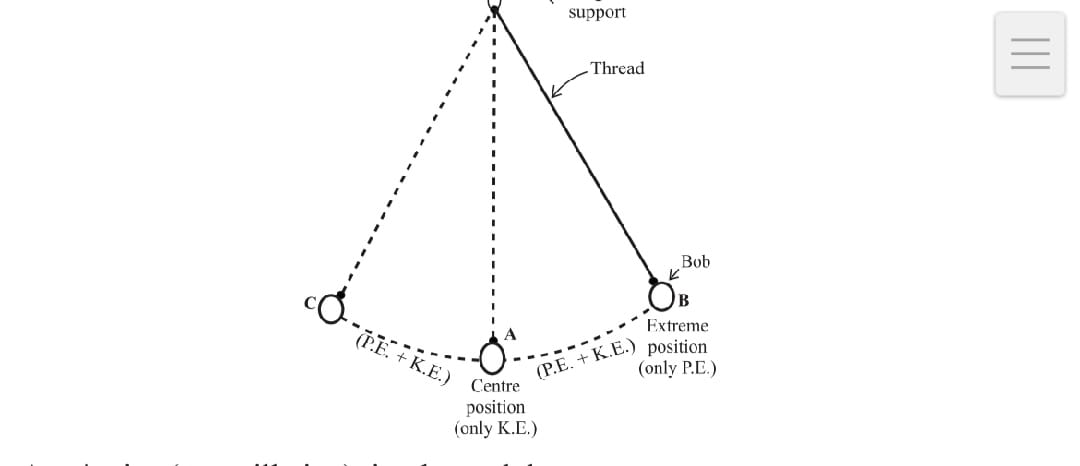
POWER : The rate of energy consumption is called power .
Power = work done/ time taken
SI unit is Watt = Joule/sec
when one joule of work done in one sec than the power consumed is one watt
1 kilo watt =1000 watt
1 Horse power = 746 watt
Example : 20 joule of work done in 5 sec than power is =20/5 = 4 watt
I kilowatt hour = 3.6 x 10^6 joule = one unit of electrical consumption.
Example : A bulb of 60 watt is used for 6 hrs /day for 30 day than electricity consumed
power x hours /1000 = unit
60 x30 x 6 /1000 = 10800/1000= 10.8 unit
Important Points for solution of text question of Work and Energy
1 Force of 7 N displacement made is 8meters than work done = 7×8=56 joule
2 A pair of bullocks exert the force of 114N displacement made is 15 meter than work done is force x displacement = 114 x15 =16710 joule
3.what is mass of a body when it is moving with velocity of 5m/s having kE of 25 joule
KE= ½ m×v²
= > 25= ½m×5²
==> 25=½×m×25 ==>
m= 25×2÷25 => m=2kg
what happens to kinetic Energy if velocity is doubled and than tripled
incase of doubled KE = ½m×v²= ½× 2 x 10² = 100 joule
incase of triple put m= 2 v=15 solve it
4, what work is done when body of 20kg is moving with velocity of 5m/s its velocity changes to 2m/s than
work done=½xm (v² – u²)
WD= ½×20(2²- 5²)
WD= 10 (4-25)=10x-21= -210 joule
5.A household the 250 units/ month than energy consumed
1 unit = 3.6x 10^6 than 250×3.6 x1000000=900×1000000 joule
6 A mass of 40kg taken to heighof 5 meter than potential energy PE=mgh = 40x10x5= 2000j
7 The energy consumed by 1500 watt heater working 10 hours P.t = 1 500x 10= 15000÷1000= 15 kwh
Conclusion: Work and Energy
Work and Energy is the chapter from physics consist the very basic idea of work and energy which covers the syllabus of class 9 with some numerical and practical examples .Work is the product of force and displacement .Energy in different form Kinetic and Potential Energy With basic idea of power .
Follow Us on: Facebook or Instagram
Read More: Motion in Straight line
Read More : Force and Laws of Motion