Fundamental unit of life Cell
The Fundamental unit of life Cell is the Chapter of biology of class 9th which covers the detail and basic idea of the functional fundamental unit of life covering the complete syllabus of the class.
CELL ;
It is the basic structural and functional unit of all form of life .All living forms are composed of microscopic units called cell The study of structure and composition is called Cytology.
Cell was first discovered and observed by ROBERT HOOKE in a thin dead slice of crock in year 1665 .
First living cell was discovered by A. V. LEEUWENHOCK in 1674 .
Protoplasm is an aggregate of various chemical such as water, ions, salts and other organic molecules like proteins , carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids, vitamins . Presents in cytoplasm along with cell organelles and nucleus that constitute a cell . It exists in sol – gel state.
CELL THEORY :
The two biologist SCHLEIDEN and SCHWANN in1838 gave the cell theory as All plants and animals are composed of cells which are the basic unit of life and arises from pre existing cell ( Viruses is the exception of cell theory )
TYPES OF CELLS : Prokaryotic cell such bacteria, blue green algae or cyanobacteria Eukaryotic as Paramecium, Amoeba , ostrich or pine tree
PROKARYOTIC CELLS :
They are very small in size about 1 – 10^-,6 m , Nuclear region is not surrounded by nuclear membrane so nucleolus are absent ,always found in unicelled organism, single chromosome is present in it Cell division by fission / budding and membrane bound cell organelles are absent such in Bacteria
EUKARYOTIC CELLS :
They are fairly large in size of 5 – 10 pico m, Nuclear material surrounded by a nuclear membrane so nucleolus is present it may be unicellular or multicellular , more than one chromosome are present cell division takes place by mitosis or meiosis. Membrane bound cell organelles are present such as all plants, animals , amoeba
ORGANISMS ARE OF TWO TYPES :
unicellular organism and multicellular organism. In the unicellular organism are single cell ,they are simple in nature ,all functions are performed by single cell , division may or may not be performed ,reproduction involved the same single cell their life spam is short . eg amoeba, paramecium, bacteria .
In case of Multicellular organism where there are large number of cells having complex , different cell perform different specific function , The specialised cells/gem cells take part in reproduction their life span is long .
CELL SHAPE :
Cells are of variable shapes ad sizes. That varies is according to their function position .Generally cell are spherical but they may be elongated as nerve cell ,branched as pigment discoidal in RBC spindle shaped as muscle cell .
It has squamous epithelium cells , Ciliated epithelium form Trachea, columnar cells in the stomach, smooth muscle that form intestine, Red blood cells/Erythrocytes , WBC, Nerve cell , sperm and ovum .
CELL SIZE :
The size of cells is variable depending upon it’s position and function. Some are microscope while some are visible with naked eyes.
Their size may vary from .2 pico m to 18 pico cm.
Size of typical cell in a multicellular organism ranges from 2 – 120 micron .
The largest cell is Ostrich egg (15cm x13cm ) weight 1.4kg The longest cell is nerve cell up to 1 meter the smallest cell so far known as PPLO as mycoplasma .
COMPONENT OF CELLS :
There is an occurrence of division of labour within a EUKARYOTIC cell as they all got certain specific components called cell organelles.
Each of them perform a specific function .Three basic components of all the cell are the plasma membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm.
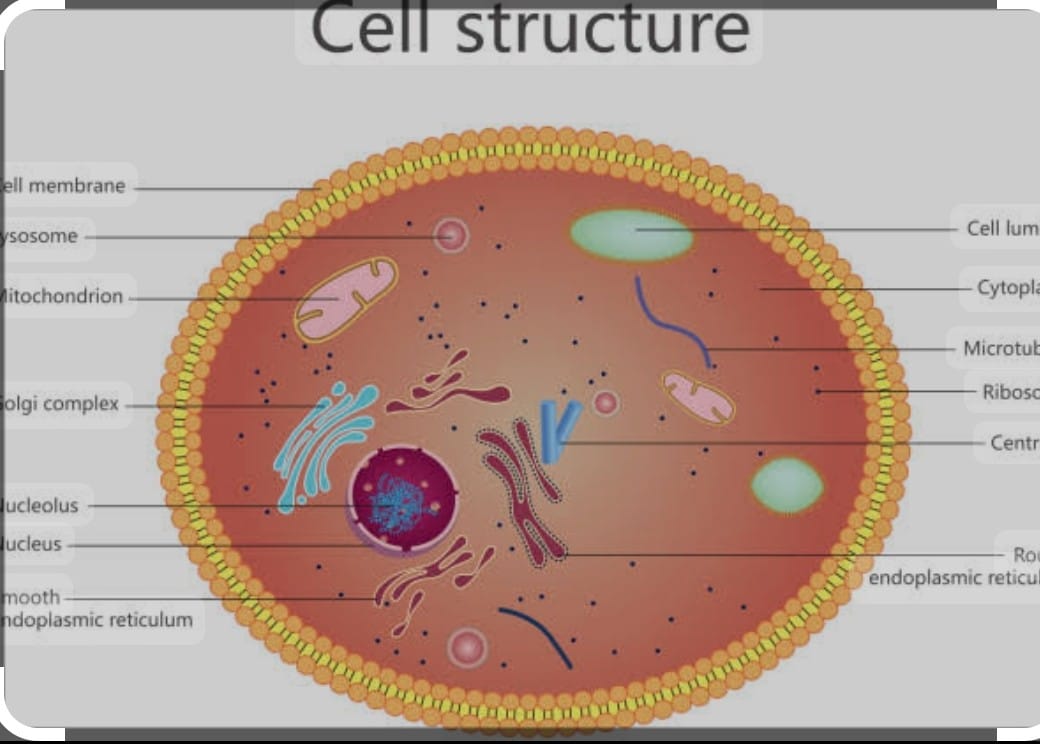
CELL MEMBRANE/ PLASMA MEMBRANE :
Plasma membrane is selectively permeable in nature , means it allows or permits the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell. The cell membrane is also called plasma membrane/plasma lemma.
It is the limiting boundary of each cell which separates cytoplasm from its surroundings. It is found in both plant as well as animals cells. It is the outermost covering of the cell incase of the animals and lies below the cell wall incase of plants . As per lipid model of plasma of plasma membrane.
It is made of proteins and lipids where proteins are the sandwiched between bilayer of lipids SINGER AND NICHOLSON gave the fluid mosaic model or lipid bilayer model of plasma membrane. It is flexible and can be folded, broken and reunited
FUNCTIONS :
It regulates the movement of the molecules inside and outside the cell , it helps in maintaining the distinct composition of the cell
TRANSPORTATION OF MOLECULES ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE :
Diffusion is the movement of solutes/ ions from the region of higher concentration to lower concentration ,it does not require any energy so it is called passive transport it do not require any semipermeable membrane
Osmosis is the movement of solvent/ water from higher concentration to lower concentration solvent through semipermeable membrane . In other words the movement of water across semipermeable membrane is also osmosis It is also called diffusion of solvent.
There are two kinds of osmosis
i) Endosmosis in which the movement of solvent into the cell takes place
ii) Exosmosis in which the movement of solvent takes place outside the cell
Types of Solution
a) Isotonic Solution in this kind the solution in which concentration of the solution outside the cell is equal to the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cell
b) Hypertonic Solution is the solution in which the concentration of the solution outside the cell is more than the concentration of the cytoplasm of the cell due to this cell loses water and become plasmolyzed
c)Plasmolysis is the shrinking of the protoplasm away from the cell wall due to loss of water (exosmosis )
d) Hypotonic Solution is that kind of solution where the concentration of the solution out side the cell is less than the cytoplasm of the cell due to which water flows inside the cell get swell or may burst
Cell Wall
It is the outermost covering of the plant cells and te cell of fungi but absent in animal cells. Cell wall is rigid , strong, thick porous and non living structure. In plants it is made up of cellulose and hemi celluloses.
In Fungi it is primarily made up of chitin. Cell walls of two adjacent cells are joined by a layer called middle lamellae and microscopic channels known as plasmodesmata for transport
Functions :
The cell wall provide strength definite shape, structure , support and protection of the cell It is permeable and allows the entry of molecules of different sizes and control intercellular transport.
NUCLEUS :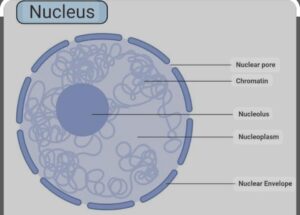
It is the most important cell organelle which directs and control all cellular activities, also called headquarters of the cell/ controller of cell discovered by ROBERT BROWN IN 1831
It is well defined in EUKARYOTES but absent in PROKARYOTES.
( It contain primitive nucleus called Nucleoid ) The Nucleus has double layered covering called nuclear membrane and also contain nucleolus and chromatin material which is made up of DNA (DEOXY RIBONUCLEIC ACID ), Protein which condense to form chromosome .
These Chromosome/ chromatin consist of DNA which stores and transmits the hereditary information for the cell function, growth and reproduction. The functional segment of DNA is genes
Function :
It directs and control all the metabolic activities of the cell and regulate the cell cycle , it also help in transmission of hereditary characters from the parents to the offsprings
CYTOPLASM :
It is the fluid content enclosed by plasma membrane discovered by KOLLIKER IN1862 It is the site of both biosynthetic and catabolic pathway ie metabolic activities
It is divided in two parts
a) Cytosol which is aqueous soluble part contain various fibrous proteins forming cytoskeleton containing water , protein , carbohydrate
b)Cell Organelles it is the living part of the cell having definite shape , structure and function bounded by plasma membrane
Single membrane bounded cell organelles are ER , Lysosomes , Golgi bodies , Vacuoles and peroxisomes
Double bounded cell organelles are mitochondria , plastids ( they have their own DNA material )
Non membrane bounded cell organelles are Ribosome , Centrosome and microtubules.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM :
It is the net work of the membrane bound tubules and sheet present in cytoplasm. Discovered by GARNIER and structure was given by Porter Claude and Fullum. These are present in all cells except prokaryotes and mammalian erythrocytes.
ER are of two type
a) SER ( smooth endoplasmic reticulum ) mainly made up of tubules , it helps in steroid , lipids and polysaccharides synthesis and ribosomes are absent in it
b) RER ( Rough endoplasmic reticulum) which is made of Cisternae and vesicles , helps in protein synthesis and contain ribosomes on the surface .
FUNCTION :
It is the organelle which serve as a channel for the transport of material between various regions of cytoplasm and its nucleus .
It also work like cytoplasm framework to provide surface for some of the biochemical activities it form endoskeleton of cell.
Itis also in the synthesis of fats, protein , steroids cholesterol SER plays important role in detoxification of drugs and poisonous products It is the membrane of biogenesis protein, lipids produced by ER are used to produce cell membrane .
GOLGI BODIES :
It consist of the system of the membrane bounded fluid filled Vesicles arranged parallel to each other in the sack called Cisternae along with some large and spherical vesicles. It was discovered by CAMILLO GOLGI It is absent in prokaryotes , mammalian RBC and sieve cells
FUNCTION ;
The main function is storage, modification, packaging and secretion of products in vesicles. It involves in the formation of lysosomes . It is secretary in nature and helps in melanin synthesis and helps i the synthesis of cell wall and plasma membrane.
MITOCHONDRIA :
It is round shape structure found in cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells except mammalian RBC and also absent in prokaryotes It was first seen by KOLLIKER in the insect cells in 1880 It is also called Power House of cell or storage battery .It is double membranous structure where the outer membrane has specific proteins while inner membrane is folded inside to form the chamber called Cristae It has it’s own DNA and Ribosomes .
FUNCTION
The main function is to produce, store and release the energy in the form of ATP ( Adenosine Triphosphate ) the energy currency of cell , it is the site of cellular respiration (Kreb cycle) in which ATP is produced .
RIBOSOMES ;
It is the site of protein synthesis all structural and functional protein/ enzymes coded by nuclear DNA are synthesized upon cytoplasmic ribosomes .The DNA codes are transcript into messenger RNA (mRNA) ( Ribonucleic acid ) molecules, which comes out of Nucleolus and translated protein synthesis by ribosomes attached to RER in the formof protein.
FUNCTIONS : They are main site of protein synthesis which is transported to ER.
PLASTIDS :
It is double membrane ,discoidal structure, found mainly in algae and plant cells , beside being discoidal /rhombic in plant cells they are present in variable shape like in the algae .They may be Coiled , Spiral or ribbon shaped .They also have their own DNA .
They are of three types
a) LEUCOPLAST :
They are white/ colorless and found in non photosynthesis tissue of plants such as roots, bulb seeds , they change into other type of plastids it’s primary function is the storge of starch, oil , proteins
b) CHROMOPLAST
They are coloured plastids except green , it imparts colour to fruits and flowers
c) CHLOROPLAST ;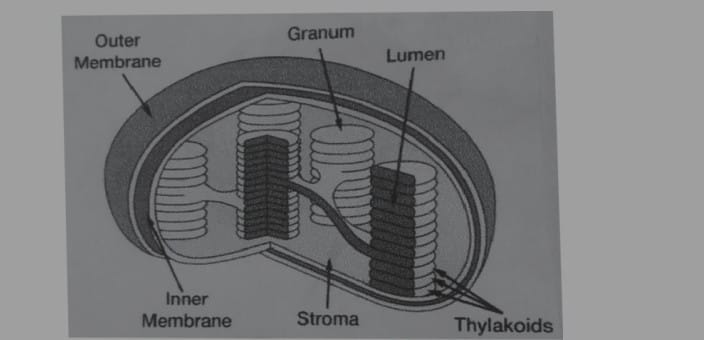
It contain chlorophyll which impart green colour to the leaves and found in aerial parts of plants it helps in the process of photosynthesis so it is also called Kitchen of the cell , It is of two type
i) GRANA which constitute lamellar system. these are founded on the top of each other. These stacks are called Grana . Each granum of the chloroplast is formed by superimposed closed compartment called Thylakoids they are the site of light reaction of photosynthesis as they contain the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll, photosynthetic units
ii) STROMA :
It is granular transparent substance is called matrix . Grana are embedded in it, it also contain lipids droplets, starch grains and ribosomes
VACUOLES :
These are membrane bounded region in the cytoplasm contain water and other substances .It is bounded by single membrane called Tonoplast .
In animals it is absent or of very small size In plants there is single large vacuole is is found which occupies 90% of the volume of the cell
It’s main function that it helps in maintaining osmotic pressure in cell and stores toxic metabolic products/ wastes products, water , sugar and protein
LYSOSOMES / SUICIDAL BAGS
They are tiny single membrane bound cell organelle contains powerful digestive enzymes for intercellular digestion , It is absent in RBC It is synthesis by Golgi bodies and enzymes present in it and are synthesis by RER
FUNCTION
Their main function is digestion, it means they break down worn out cellparts,they are the kind of waste disposal system of the cell It also help the digesting the foreign material like viruses and bacteria invaded in cell .
SUICIDAL BAGS :
During the disturbances in cellular metabolism / cell damage Lysosomes burst and their enzymes are released into cytoplasm which digest the own cell therefore it is known as suicidal bag.
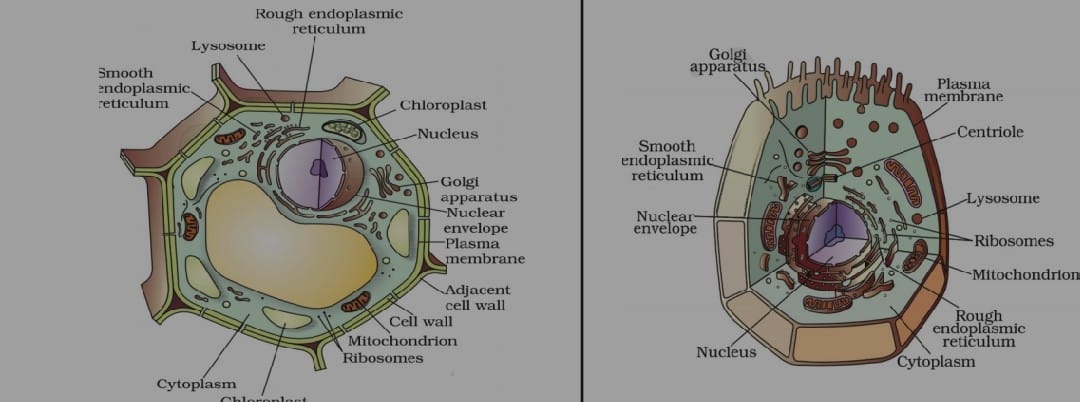
PLANT CELLS ;
They contain chloroplast for photosynthesis, It have a cell wall to maintain it’s structure and rigidity , usually do not have lysosome and peroxisomes, cells are square and rigid /geometrical shape it has large central vacuoles
ANIMAL CELL ;
It has chloroplast ,no cell wall , may contain cilia and flagella , cells are fluidic and flexible in shape it has very small or no vacuoles but have lysosomes.
CELL DIVISION :
New cells are formed in the organism to relace dead cell/ old cells/ order to grow/ injured cells and to form gametes for reproduction . The process by which new cells are made is called division of cell.
They are of two type
a) MITOSIS
It is the process of cell division by which most of the cells divide for the growth is called mitosis. In tis process , each cell called mother cell divides to form two identical daughter cells. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the mother cell it helps in growth and repair of tissue in organism
b) MEIOSIS
In this specific cells of reproductive organs/ tissue in animals and plant divide to form gametes, which after fertilization give rise to offsprings . They divide by different process called meiosis which involve two consecutive divisions.
When cell divides by meiosis it produces four new cells instead of two . The new cells have only half the number of chromosomes than that of mother cells and these new cells are transformed into gametes .
CONCLUSION : Fundamental Unit of Life Cell
In the Chapter Fundamental unit of life Cell covers the detail syllabus of class 9th with basic idea of cell , Organelle and their function which is very helpful to medical aspirants .
Follows us on : Facebook
Read More : Tissue