How do Organisms Reproduce
How do Organisms Reproduce is the Chapter from Biology that covers the syllabus of Class 1o giving the basic idea of Reproduction of different organism and plants.

-
- REPODUCTION is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves.
- It ensures continuity of life on the earth, It enridges to transmission.
- It involves the continuation of characteristics from the parents to daughter cells by copying of deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) these are the molecules present in the chromosomes of the nucleus of the cell. The DNA in nucleus is the information source of Protein. By reproduction there is creation of DNA and chemical reaction builds the copies of DNA in the cell, two copies of DNA cell is produced in reproducing cell. The cell divides to give rise two cell.
- It is not the the perfect exercise as DNA cell copies are similar but not identical to original.
- Small change brings out the variations in the offspring Useful variation are retained but the harmful don’t.
- The variations help the species to adapt in drastic environmental change therefore save the species from being extinct and promote them to survive and also help in evolution.eg Bacteria living in temperate water if temperature rises by global warming these bacteria would die but few variant resistant would survive.
- There are two types of reproduction found in the organism.
- ASEXUAL REPRODOCTION which require a single parent they are a) Fission b) Budding c) Fragmentation d) Regeneration e) Spore formation f) vegetative propagation.
- SEXUAL REPRODUCTION requires two parents this kind of reproduction can be found in plants and animals including human being
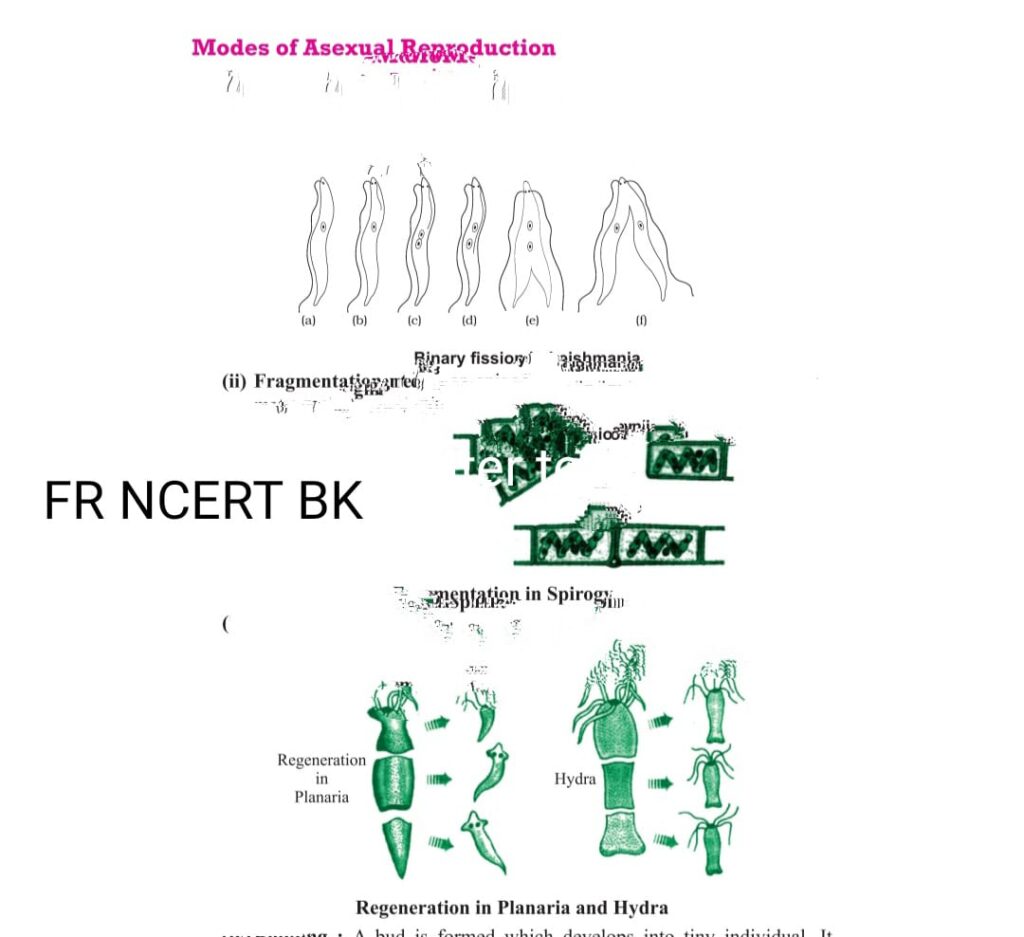
- FISSION in this kind of reproduction a cell divides into two cell (Binary fission) it may be transverse binary fission eg Aomeba or longitudinal binary fission Leishmania or more cells which is multiple fission eg Plasmodium.
- FRAGMENTION in this kind of reproduction breaking into two or more fragments eg Spyrogyra+
-
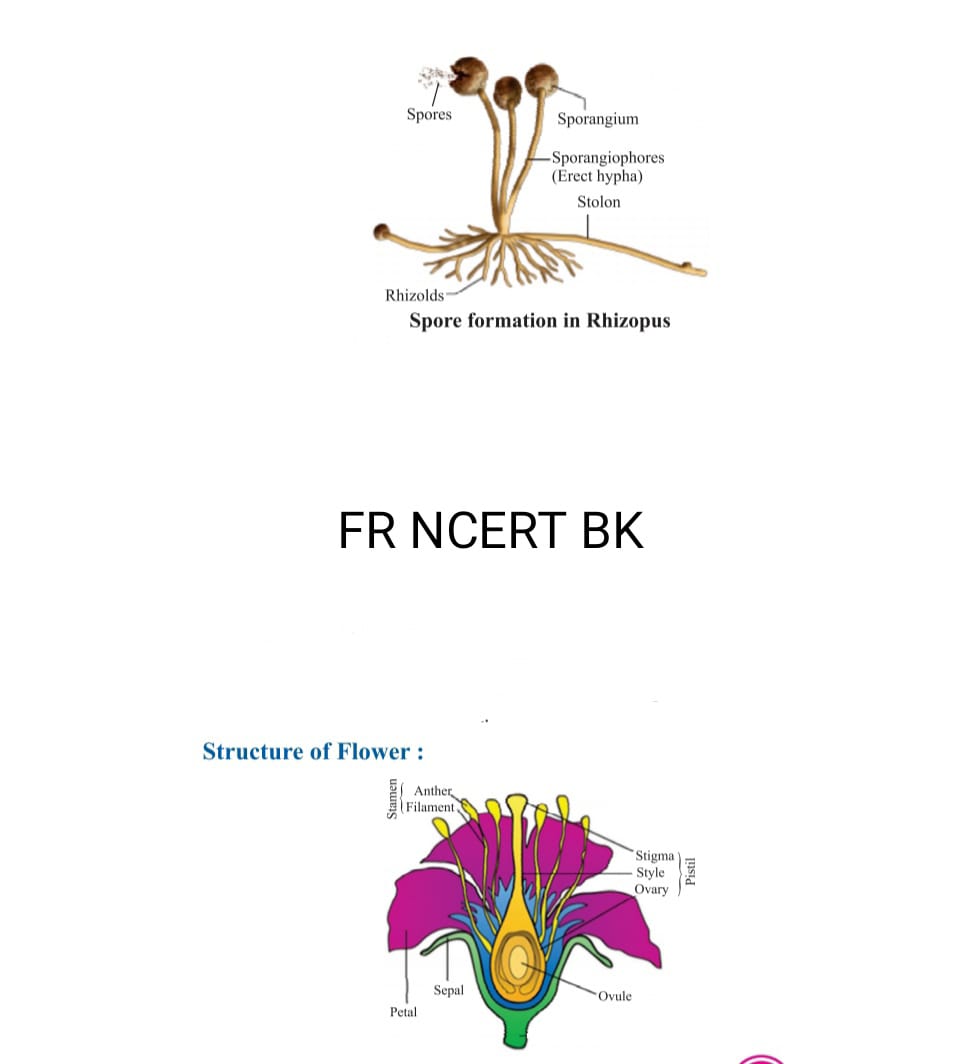
- SPORE FORMATION in this kind of reproduction spores covered by hard coat so as to face harsh environmental condition eg fungi
- REGENERATION in this reproduction simple animals like Hydra, Planaria develop a individual from their broken older parts, it is carried out by specialized cells which grow large number of cells
- BUDDING in this kind of reproduction a new organism is produced as the outgrowth of the parent part of the body’s
- VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION It is a mode of reproduction in which new plants are formed from its vegetative parts such as
- a) roots el dahlias, sweet potato,
- b) by stem eg potato ,ginger
- c)by leaves eg in which leaf notches bear buds that develop into new plants
- ARTIFCAL METHOD
- 1)grafting in mango
- 2)cutting in rose
- 3) layering in jasmine
- TISSUE CULTURE in this method new plants are grown by using growing tips of plants. These growing cells are kept in the culture medium leads to the formation of cells then these is transferred to hormone medium which help to grow in new different plant eg orchid decorative plants.
- THERE are lot of benefits of tissue culture
- 1) we can grow those plants which do not have capacity to produce seeds such as Banana, rose, jasmine and these are similar to parental plants.
- 2) It also help in growing seedless fruits.
- (NOTE : ABOVE FIGURE FROM NCERT BOOK CLASS X)
- SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
- In this type of reproduction two parents are required male and female this reproduction occurred when the fusion between two gametes take place. this is the process of fertilization
- When there is exchange of chromosomal fragments between homologous chromosomes which cause genetic recombination produce variation
- SEXUAL REPRODUCTIN OF PLANTS
- The reproductive organ of plant is flower, there are four main whorls
- a)sepals
- b)petals
- c)stamen
- d)pistil
Flowers are of two type a) Bisexual in which both male and female are present as a reproductive organ eg Lilly, tomato mango, sunflower. brinjal, hibiscus b) Unisexual flower in either male or female work as reproductive organ ,eg bitter ground, pumpkin cucumber, papaya
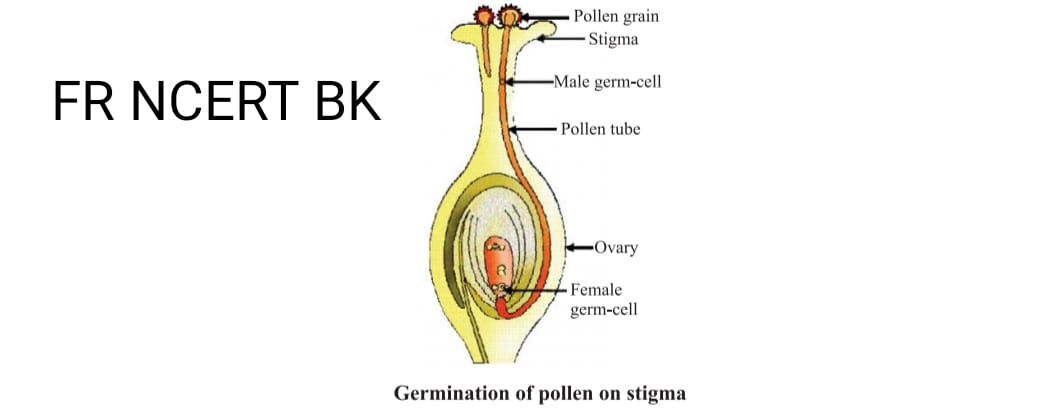
Reproduction in the flower takes place transference of pollen grains
-
- When the pollen grains of the flower transfer to stigma of the carpel of the same flower it is self-pollination
- When the pollen grains of one flower transfer to stigma of the carpel of another flower it is called cross pollination.
- The cross pollination is possible through means of , triennials, wind and water..
- When pollen grains germinate it form a pollen tube than it passes through style finally goes to ovule in ovary
- Here the fusion of male and female gamete which is present in ovule takes place this is called FERTILISATION.
- Zygote is formed in ovary and this zygote divides to form Embryo.
- Thick coating is formed over ovule gradually becomes seed and finally ovary changes into fruits
REPRODUCTION IN HUMAN BEING
- REPRODUCTION in case of human being is sexual mode of reproduction. When the human become mature for sexual reproduction it is the period of life when germ cells are produced in both i.e. ova in case of female and sperms in case of male. This sexual maturation in male or female youngsters is called puberty. In this there are some changes in the body of both boys and girls.
- The common changes that we notice in both gender A)Growth of hairs in armpits and on the genital aera. B) Skin becomes oily with pimples
- Changes in boys such growth of hair on face,, voice become thick and crack.
- changes in girls as increase in breast and menstruate.
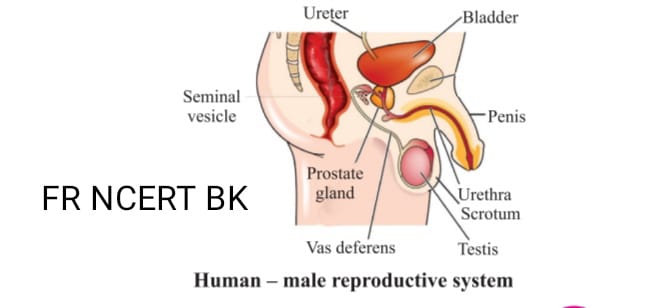
MALE REPRODUCTION SYSTEM
-
- There are four major parts. in male
- 1) Testes
- 2) Vas deferens
- 3) Urethra
- 4) Glands
- Testes A pair of testes located inside scrotum present outside the abdominal cavity. because it needs lower temperature for production of sperms. It also releases testosterone the male hormone. responsible for puberty and sperms.
- Vas deferens it is tube like passage to take sperms to urethra
- Urethra is the outer covering of penis and common passage for urine and sperms.
- Prostate glands and seminal vesicles releases fluid that nourishes. sperms for easy transportation. with secretion. glands it makes semen.
FEMALE REPODUCTION SYSTM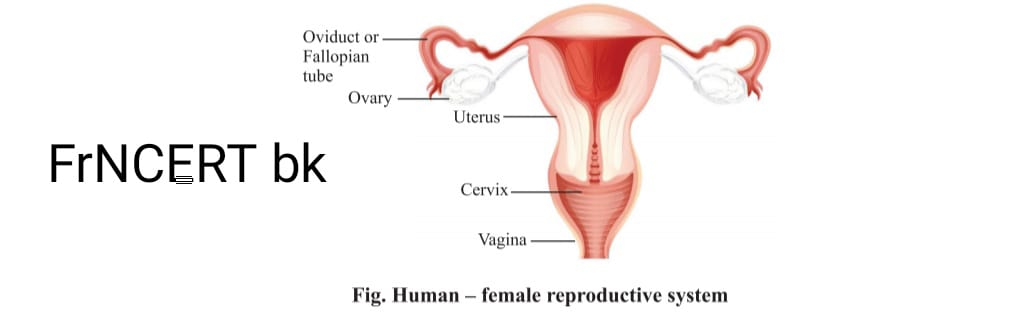
- Female reproduction consists of major the parts
- 1) Ovary
- 2) Fallopian tube
- 3) Uterus.
- There is pair of ovaries which is present on both side of abdomen. Germ cells or eggs are produced here. Thousands of immature eggs are there in ovary during the time of birth of baby girl .At the time of puberty some eggs start maturing it is estimated that every month each of the get matured.
- Fallopian tube it is also called oviduct that receives the egg produced by the ovary, transfer it to uterus where fusion takes place gametes.
- Uterus. is a bag like structure where fertilization and development baby takes place after implantation of embryo this uterus opens into vagina by means of cervix.
- When the sperms of male fuses with eggs of female the fertilization is caused, it form the zygote in uterus, further develop into embryo.
- It gets nutrition from the mother blood through Placenta a special kind of tissue.
- This Placenta provides a large surface area for the exchange of oxygen, glucose, waste material
- nine months are taken from the fertilization to the birth of child this is called Gestation period
MENSTRUATION CYCLE
There is thick and spongy support to the embryo. If fertilization had not taken place lining is not needed therefore break out in vagina as blood and mucus this takes place after every 28 days
- Uterus gets ready itself to receive the fertilized egg so the lining of uterus become in month, so it is called MENSTRUATION CYCKE.
- Reproductive health is very important for reproduction that is well being of both the genders with respect to physical ,social, behavioral manner.
- STD means sexually transmitted disease. They are of two kinds
- 1) Bacterial eg GONORRHOEA, SYPHILLS
- 2)Viral eg WARTS , and HIV-AIDS if user use condoms, then can be prevented to some level.
- Contraception is the method to avoid pregnancy egg may not fertilized.
- There are various methods of contracepts
- a) Physical Method use of condoms, cervical cap and diaphragm to prevent the union of egg and sperms.
- b) Chemical method by using oral pills which creates hormonal balance of body, so eggs are not released but this has some side effects
- c) IUCD means Intrauterine contraceptive device in this copper T or loop is placed in uterus for prevention
- Surgical Method
- 1. Vasectomy in this male vas deferens is blocked. 2)Tubectomy in this fallopian tube is blocked in female
- Female Feticide it is the bad practice of killing female child in the womb of mother. If we have balanced sex ratio, will have healthy society for this we have to educate people to avoid this malpractice Prenatal sex determination is purely illegal.
-
Conclusion :How do Organisms Reproduce
Organisms reproduce through a various methods, which are of two main types: sexual and asexual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material from two parents, typically through the fusion of specialized reproductive cells called gametes. This process increases genetic diversity within a population, which can enhance adaptability and survival.
Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, involves a single parent producing genetically identical offspring , but it doesn’t introduce genetic variation. Common forms include binary fission in bacteria, budding in yeast, and vegetative propagation in plants.
Read More : Heredity and Evolution
- Follow us on: Facebook
- Follow us on : Instagram