India Size location and Physical Features
India Size location and Physical Features is the Chapter of Geography that covers the syllabus of class 9th with basic idea of size of India location and Physical nature of India.
India Size location and Physical Features
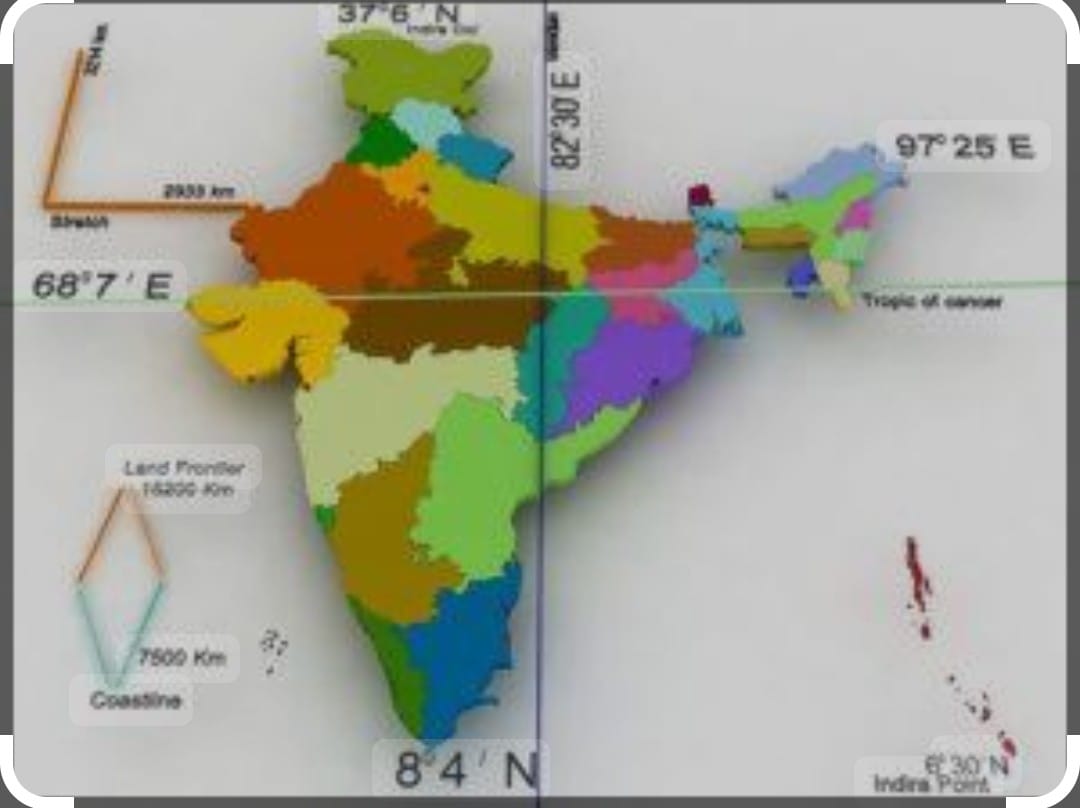
The population of India is about 142 crore ,is about 17.5%of the world’s population and having second position after China. The a geographical aera of India is 32.8 lakh sq km which is 2.4% of the land space of the world and seventh position in the world after Russia, Canada, USA, China ,Brazil and Australia.
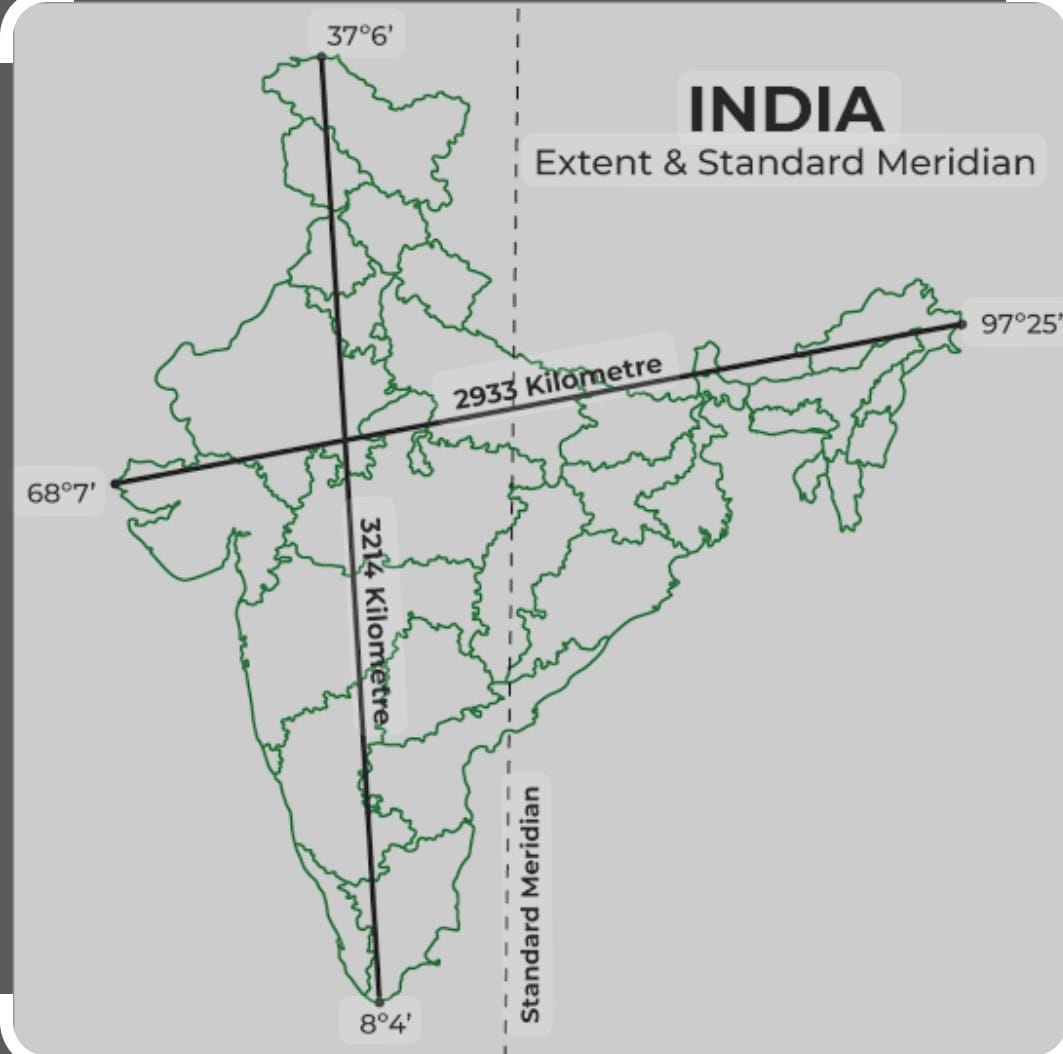
India has 28 number of states and 08 union territories , with land boundary of 15200km Total length of coastline including Andaman and Nicobar as well as Lakshadweep Islands is7516.6 km .Standard Meridian of India is 82degr30’E and it passes through Mirzapur (UP) Latitudinal extent of India is 8deg4’N to 37 deg6’N where as longitudinal extent is 68 deg7′ E to 97deg25′
India’s Neighboring countries are Pakistan , Afghanistan lies in the north east of India . China, Tibet , Nepal and Bhutan in the north of India Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east and Sri Lanka in the south of India.
Pakistan touches Jammu and Kashmir , Punjab , Rajasthan and Gujarat. Jammu Kashmir , Himachal Pradesh Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh touches China, Arunachal Pradesh , Nagaland Manipur and Mizoram touches Myanmar, Bangladesh touches West Bengal, Mizoram. Meghalaya , Tripura and Assam . The Palk of Strait is the channel between India and Sri Lanka . Maldives lies in the south of Lakshadweep.
The Tropic of Cancer at 23 deg 30′ passes India and divides into two halves , it passes through Gujarat, Rajasthan Madhya Pradesh , Chhattisgarh , Jharkhand , West Bengal ,Tripura , and Mizoram (8 states ) .
The largest states is Rajasthan in terms of aera the smallest states in term of aera is Goa .Total length from North to south is 3214km and breath from East to West id 2933km .
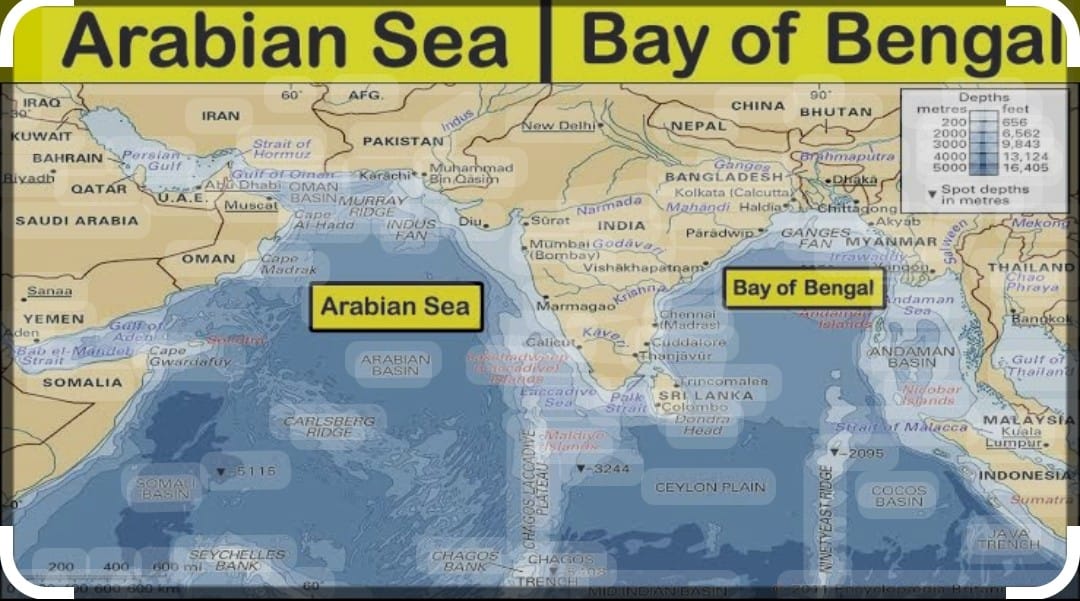
The group of Islands of India located in the Bay of Bengal is Andaman and Nicobar Islands where as in Arabian Sea is Lakshadweep Islands. The Ocean which has been named after our country is Indian Ocean
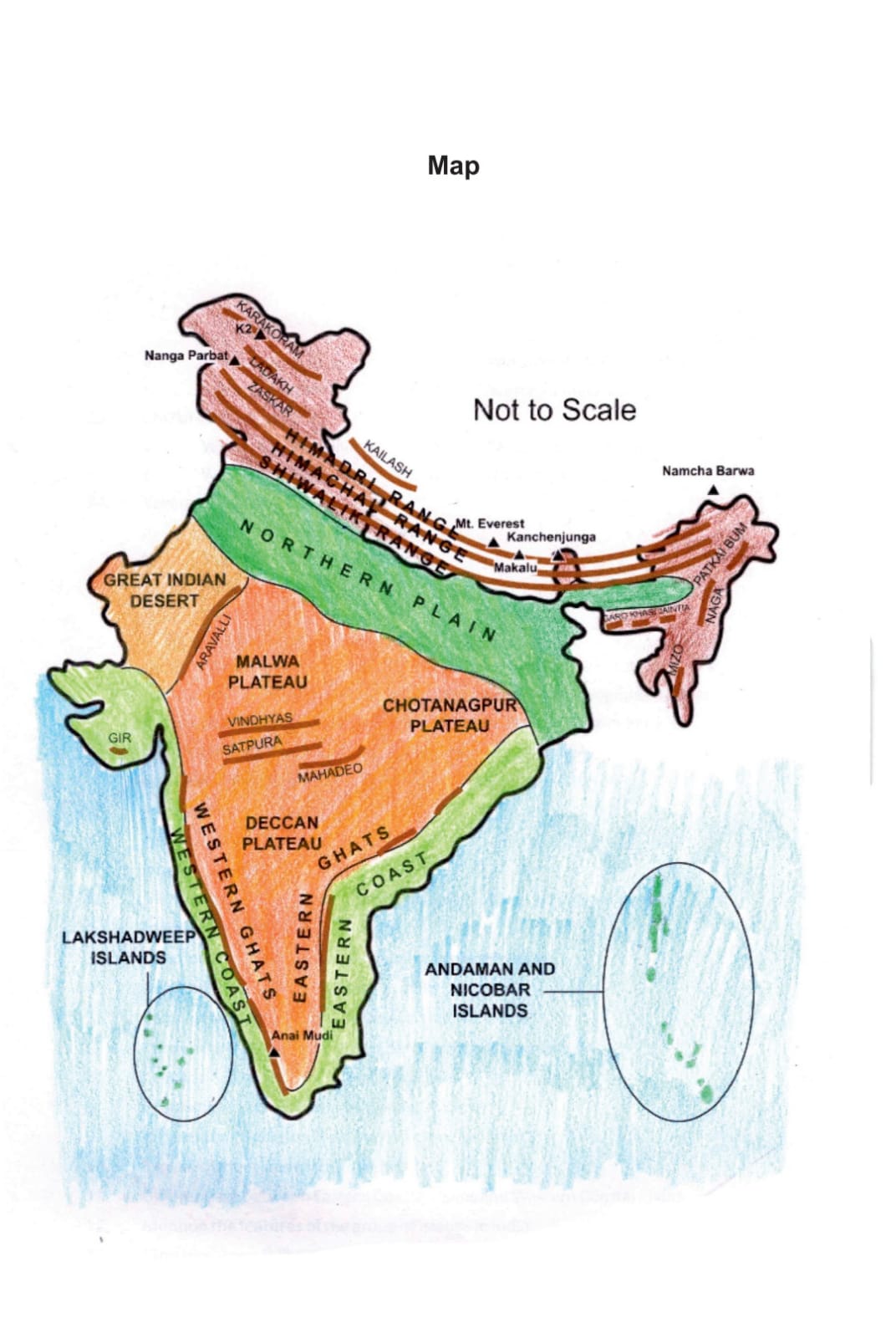
PHYSICAL FEATURES
THE HIMALAYAN MOUNTAIN :
It is the young fold mountains stretch over the northern borders of India , It’s total length is 2400km with is 400km in Kashmir to 150 km in Arunachal Pradesh .
The Himalayas consist of three parallel ranges in it’s longitudinal extent
a) Great/Inner Himalayas or the Himadri :
It is the northern most range of the Himalayas It is the most continuous range and contains all the prominent Himalayas peaks with the average height of 6000 meters some of the highest peaks are the mount Everest, Kanchenjunga , Makali , Naga Parbat .
b)Lesser Himalayas /Himachal :
It’s altitude varies from 3700 m to 4500 m . Pir Panjal , Dhaula Dhar and Mahabharat are the important ranges .The famous valleys as Kashmir, Kullu and Kandra lies in this aera.
c) Shivalik’s :
This is the outermost ranged of the Himalayas The altitude varies between 900 to 1100 meters The longitudinal valley lying between lesser Himalayas and the Shivalik’s are known as Duns , Dehra dun , Kotli Dun and Patli Dun are some important known as Duns.
The Himalayas have been divided on the basis of region west to east
These are
a) The Punjab Himalayas lie between Indus and Sutlej rivers
b) Kumaon Himalayas lies between lie between Sutlej and Kali rivers ,
c) Nepal Himalayas lies between Kali and Tista rivers
d) Assam Himalayas lie between Tista and Dihang rivers
e) Purv Anchal Himalayas : is extended along the eastern border of India
THE NORTHERN PLAIN in India size location and Physical Features:
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the three major river system such as The Indus , the Ganga ,and the Brahmaputra along with their tributaries . The plain is formed of alluvial soil . It is agriculturally a very productive part of India .
The northern plain is broadly divided the three sections
a) Punjab Plains This is the western part of the northern plain. It is formed by the Indus and its tributaries the Jhelum ,the Chenab the Ravi the Beas and the Sutlej. This section of the plain is dominated by doabs.
b) The Ganga Plain : It extends between Ganga and Yamuna rivers . The is spread over the states of Haryana , Delhi , UP , Bihar Jharkhand and West Bengal
c) The Brahmaputra Plain : The Plain is formed by the Brahmaputra and it’s tributaries . It lies mainly in the state of Assam.
The Northern Plain can be divided into four regions according to the variations in relief features :
a)Bhabar This region lies parallel to the slopes of the Shivalik. The rivers , after descending from the mountains deposits the pebbles in this region. All the streams disappear in this bhabar region
b) Terai It lies to the south of bhabar . The streams and rivers re-emerge here .It is wet, swampy and the marshy region
c)Bhangar is the largest part of the northern plain and is formed of the oldest alluvial soil .They lie above the flood plains of the rivers and present a terrace like feature. The soil in this region contain calcareous deposits locally known as kankar
d) Khadar It is the flood plains formed by newer and younger depositsare called Khadar. They are renewed almost every year and so they are fertile.
THE PENINSULAR PLATEAU :
It is composed of the old crystalline, igneous and metamorphic rocks . It was the part of the Gondwana Land thus making the part of oldest landmass. It consist of two region
i) Central Highlands ii) Deccan Plateau .
The black soil aera of the peninsular plateau is called Deccan Trap This is a volcanic region so there are igneous rocks.
The Indian Desert lies towards the western margins of the Aravalli Hills .It is an undulating sandy plain covered with sand dunes. This region receive very low rainfall below 150mm/year , having arid climate with low vegetation .
Streams appears during rainy season . LUNI is the large river in this region . Barchans a crescent shaped dunes cover larger aeras of the Indian Desert.
THE COSTAL PLAINS in India Size location and Physical Features :
It is divided in two forms western coast and eastern coast
The Western Coast :
It is located between the western ghats and the Arabian sea, relatively narrow . It consist of three sections the northern part of the coast is called Konkan , the central stretch is called Kannad Plains while the southern part is called Malabar coast.
The Eastern Coast :
It lies between the eastern ghats and the Bay of Bengal . It is comparatively wider .It is divided in two parts the north part is called Northern Circar where as south part is called Coromandel Coast .
The Large rivers like the Mahanadi, The Godavari The Krishna and the Kaveri form extensive delta on the coast . The Chilaka lake is the largest salt water lake in the state Odisha
The western and Eastern ghats are the marks of their respective edges of the Deccan Plateau
.a) Western Ghats lies along the Arabian sea . They are continuous and can be crossed through passes , average height is 900-1600 meters The highest peak is Anai -Mudi (2695 meters)
b) Eastern Ghats lies along Bay of Bengal, they are discontinuous , irregular and dissected by the rivers ,their average height is 600 meters the highest peak Mahendragiri (1501 meters)
The Islands :
a)Lakshadweep Islands :
This group of islands is composed of small coal islands which cover a small aera of 32 sq km. Kavaratti island is the administrative headquarters of the island It has diverse flora and fauna for which it is famous .
b) The Andaman and Nicobar Islands :
These islands are located in the Bay of Bengal extended from north to south The entire group of islands are divided into two broad category The Andaman in the north and the Nicobar in the south .
It is believed that these islands are elevated portion of the submarine mountains These islands lie very close to equator and experience the equatorial climate and have thick forest cover.
Conclusion :India Size location and Physical Features
India Size location and Physical Features are a vast and diverse country, mainly located in South Asia.
India size location and Physical Feature have unique geographical position, the Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea, and Bay of Bengal, has sharply influenced its history and culture.
India’s varied landscape having the mighty Himalayas in the north, expansive plains in the center, and a long coastline in the south.
The country’s size and location have contributed to its rich biodiversity and climate variations. From snow-capped mountains in North to tropical beaches in south, and from arid deserts of Rajasthan to lush rainforests of east ,
India’s physical features gives the idea of a remarkable range of environments. These diverse lands have influenced the country’s agriculture, economy, and way of life.
Follows on : Facebook
Follow on; Instagram
Read More: Drainage in India