Indian Economics part 2
In this chapter of Indian Economics Part2 Problem of unemployment and it’s components are discus which covers the syllabus of class 12.
GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT,(GDP)
It is the total money value of all goods and services produced in a country in a year
GROSS NATIONAL PRODUCT(GNP)When earnings from the foreign transaction ie net factor income from abroad is added to gross domestic product is called gross national product.
WORKERS: All those persons who are engaged in economic activities are called workers
EMPLOYMENT : It is a contract in which one person, the employee, agrees to perform work for another the employer.
POPULATION: It is defined as the total number of people who reside in a particular locality at the particular point of time.
WORKERS POPULATION RATIO =(Total number of workerx100)÷ Total population
This ratio is useful in knowing the proportion of the population contributed to the production of goods and services of a country
LABOUR FORCE PARTICIPATION RATE=(Total LABOUR forcex100)÷Total population
It is the ratio of labour force to the total population

EMLPOYMENT in Indian Economics :are all those persons who were actually employed in some kind of economic activity and are engaged in some work the labour force includes both employed and unemployed persons between the age of 14-60 years.
Work force are those people who are actually engaged in some or other economic work for their livelihood and economic development
SELF EMPLOYED in Indian Economics are those who owns and operates an enterprises to earn their livelihood whereas Casual Wage Workers are those who work in the enterprise in temporary bais and get payment for the work done by him/her. It is not sure that they always get the work during they have to face unemployment
Regular Salaried Employed are those workers working in the organised sector with good regular salary, job security and time bound work and secure future but Casualisation of work are the workers working in unorganised sectors with no job security and no time bound work
In Rural areas 64.1% of the work force are engaged in primary sectors,20.4% of rural worker force are involved in manufacturing sectors/ secondary sectors and 15.4% of rural work force are engaged in tertiary sectors
urban area agriculture or mining is not majority done in urban area but 35percent are doing the work in secondary sectors and more than 58.3% are in tertiary sectors.
We find that both men and women have different employment opportunities i) both male and female are involved and concentrated in primary sectors and number of women are more than the number of males
ii)Men have more opportunities in secondary and tertiary sectors but now a days in tertiary women are replacing menbais and get payment for the work done by him/her.It is not sure that they always get the work during they have to face unemployment
Regular Salaried Employed are those workers working in the organised sector with good regular salary,job security and time bound work and secure future but Casualisation of work are the workers working in unorganised sectors with no job security and no time bound work
CHANGING STRUCTURE in Indian economics part2
It is no doubt that India GDP grew in the postive directionsince1950-2015 and higher than the employment growth and employment grew at the rate more than 2 percent but it is the matter of great regret that the gap between GDP and employment growth started increasing
The gap has widen than more than 29 % of educated youth are unemployed which is the greatest tension for our country this trend is called jobless growth it is the situation when the economy is able to produce more goods and services without the proportionate increase in the opportunities of employment
CHANGE IN OCCUPATIONAL STRUCTURE in Indian Economics part 2:
It is fact that there has been a substantial shift from primary sectors workforce to secondary and tertiary sectors ,there has been declined in the proportion of the workforce in primary sectors because of educational unemployment and disguise unemployment
Though the employment has been classified into
a) Formal Sector Employment are those institution hire more than 10 workers completely protected through the various labour laws and get social security benefit and better wages
b) Informal sectors are those institution that and get social security benefit and better wages
INFORMATION OF WORKFORCE are the proportion of informal workers in the total workforce increases.
INFORMAL SECTORS are all those private sectors which are unorganised and contain employs less than 10 very less job security along with very less wages and no time bound of work worker working in this sectors are known as informal work force
.FORMAL SECTORS are the organised sectors of the economy which includes government department and private organisation having more than 10 workers following all regulation of government labour laws with good salary, complete job security and definite time bound of work the persons working in this sector are called formal workforce
UNEMPLOYMENT are those unemployed who are able and willing to work at prevailing wages but do not get work it is also known as open unemployment.This is classified as a)Seasonal Unemployment it is mostly found in agriculture in which people have work for sometime in a year
DISTRIBUTION OF EMPLOYMENT In the course of Indian economic part2 development of the country labour flows takes place form primary sectors to secondary and tertiary sectors such as agriculture, mining and quarrying ,manufacturing, electricity ,gas and water supply,construction ,trade, transport and storage services
Agriculture ,mining ,fisheries comes in the category of primary sectors, manufacturing of finished goods obtained from primary sectors are secondary sectors whereas service sectors which includes trade,transport, storage ,banking and other services
LOTS OF PROBLEMS are faced by informal sectors such workforce do not get regular income, they use outdated technology, accounts are not being properly maintained by the entrepreneurs and living condition of the workforce is also poor.
NATURE OF UNEMPLOYMENT
a) Rural Unemployment which includes seasonal and disguise unemployment because of improper infrastructure in farming such as improper irrigation facilities, no subsidiary employment opportunities, large dependence on labour
b)Urban unemployment this includes educated unemployment, this is due to slow increase in the opportunities, rapid expansion of education in the country, lack of vocational education
facilities and use of more capital intensive technique
c,)The Open Employment is another major problem
CAUSES in Indian Economics part 2
i) ,Our country has underdeveloped economy
ii)Rapid growth rate of population has adversely affected the unemployment situation
iii)Agriculture is the main source of livelihood and it being a seasonal occupation it does not provide work to the farmers throughout the year
iv) Our defect education system is also responsible as there is no vocational educational system for young ones to get skill and get the work for their self.
v)Economic Reforms have led to the jobless growth and decline in the cottage industry has created a massive unemployment in the country among the artisans working in the industry
vi)Shortage of capital and lack of modern technology made the generation insufficient employment opportunities in the industrial sectors
MEASURES
1)The problem of unemployment can be solved through the process of accelerated growth
2)Control of population can ensure that the additional jobs created do not fall short of new job seekers to the labour market
3)SSI and cottage industries must be encouraged along with the improvement in infrastructure facilities will enable agriculture and industrial to produce at optimum level
4)Special wages employment and self employment programmes must be introduce and encouraged
5) Development in agriculture sectors should be made to increase the productivity of labours 6)Theoretical education should be converted to vocational based
7)Measures like promotion of multiple cropping system ,good irrigation system, promotion diversified jobs be given ,along with increase in the productivity of labours
6)Theor kind of unemployment in which number of worker employed are more than it is required and productivity remain unaffected if they work or not ie more person employed than needed
7) Educated Unemployed are those who are educated and having the skill than also do not get the work at the prevailing wages and if they are get less wages than their skills and knowledge than they are called under employed
ROLE OF GOVERNMENT in Indian Economics:
a) Rural Employment Generation Program (REGP) This program aims at creating self employment opportunities in the urban aeras. Under this program , one can get financial assistance in the form of bank loans to set up small industries the generate .
b)Swarana Jayanti Shari Rozgar Yojana (SJSRY) in this program mainly aims at creating employment opportunities for both self employment and wage employment in the urban aeras . It is now called as Deendayal Upadhya Yojana .
c) Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MNREGA) under this act work is guaranteed for one member or the house for 100 days in financial year . The number of days has now been raised to 150 days/ year
d) Swarana Jayanti Gramin Swar – Rogar Yojana (SGSY) for self employment of village people to promote micro enterprises and provide assistance to self help groups .
ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT In Indian Economics part 2
Environment is the total planetary inheritance and the resources around it. In the other words it is the sum of total external forces that are around us.
It includes all the biotic factors which includes all living elements like birds, animals plants forests ,fishes and human beings and abiotic factors which included all non living elements as air, water, land ,etc They always influence each other.

THE MAIN FUNCTIONS that the environmental resources represent minerals,Woods, water,that are used as inputs in the process of production
It sustains life by providing the basic necessities of life,It absorbs the waste generated by the activities of consumption and production activities.It includes land,water bodies ,forest,which look pleasing and also improve the quality of life.
The environment is able to perform these functions as long as demand on the functions is within its carrying capacity
CARRYING CAPACITY implied two things first the extraction of resources should remain below the rate of resource generation secondly the generation of waste should remain within the absorption capacity of the environment.
STATE OF ENVIRONMENT in Indian Economics part 2 :
India has abundant natural resources in terms of rich quality of soil, many rivers, Lish green forests, plenty of mineral deposits like bauxite ,copper ,diamonds, lead ,manganese,zinc, uranium etc but despite these advantages there are some basic problems related to environment
such pollution and excessive exploitation of natural resources both these problems have emerged due to rapid economic growth and industrialisation in the developed world.[
ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT:
Environment is the total planetary inheritance and the resources around it.In the other words it is the sum of total external forces that are around us.
It includes all the biotic factors which includes all living elements like birds, animals, plants forests, fisheries and human beings and abiotic factors which included all non living elements as air,water,land,etc They always influence each other.
CHALLENGES TO ENVIRONMENT in Indian Economics part 2:
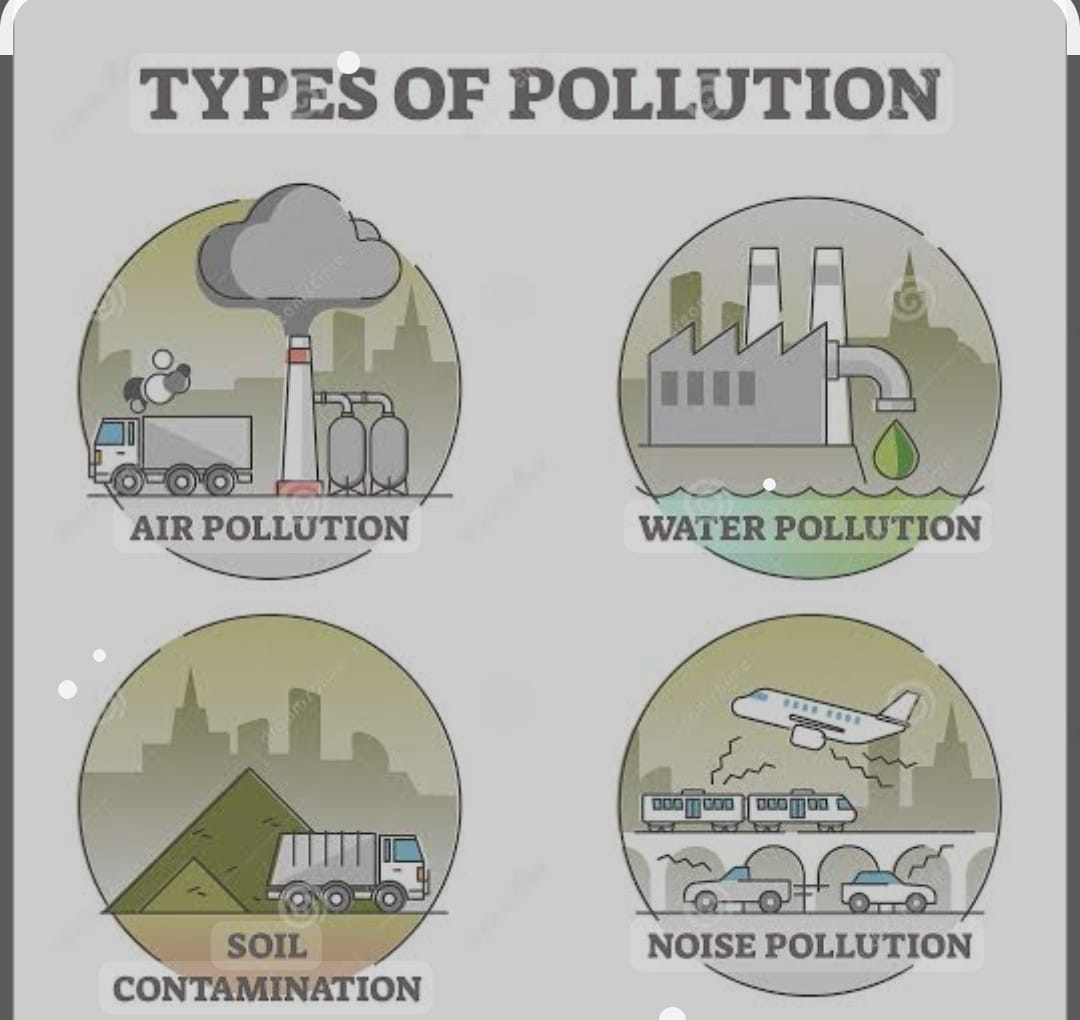
a)Air pollution indicates the presence of pollutants in the air which causes health problems it is mainly causes by industries and vehicles.
WATER POLLUTION, This means contamination of of water by foreign matter that deteriorates quality of the water. It is mainly caused by domestic sewage, industrial waste water, chemicals and pesticides used in agriculture and waste generated by thermal power houses
Noise pollution :Mechanization has raised the levels of efficiency, but it has also raised of noise pollution. Man made sources of noise pollution
DEGRADATION OF LAND It means the loss of fertility of land. It has put a huge pressure on the country’s limited land resources. SOIL EROSION It takes place when the surface of soil is washed away due to excessive rainfall and floods deforestation is the major reason for this occurance
.DEFORESTATION is the removal of. trees and forest aeras rapid amount of deforestation imbalance the ecosystem of the place and disturb the ecological balance of the country.
LOSS OF BIODIVERSITY This Included different types of plants, micro organism etc. It is very important resources because it enhances natural beauty, helps in renewing the natural resources and also helps in creation of ecological system.
CAUSES:
Rapid growth of population has put burden on natural resources, widespread poverty has led to excessive cutting of trees by poor people to be used as fuel.
Rapid industrialisation had led to severe environment problem due to generation of lots of waste .
Increasing use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides ,and insecticides has added to environmental degradation .
Urbanization has caused clearing of land for housing ,industries, construction of roads, multiplicity of transport vehicles has considerably increased as noise and air pollution .
SUITABLE MEASURE TO CONTROL
The priority must be given to vehicular pollution , It is necessary to recycle the domestic and industrial waste must be put in some productive use,
There is a need to focus on poverty issues in order to control pollution slum area must be improved with respect to sanitation , drinking water and the living aera,
The urgent need to control the population increase so the waste generated must remain within the carrying capacity. Public awareness must be spread about the ill effects of pollution and degradation of soil
. Afforestation must be encouraged in extensive manners and more public transport should be used by public and it must be made well equipped.
THE GOVERNMENT SHOULD ALSO TAKE ACTIVE PART IN this respect as they have taken many legal steps in this regard to protect the environment of the country
i) ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION ACT 1986 which empowers the government to take all necessary steps for protecting and improving the environmental conditions
ii) POLLUTION CONTROL BOARD has been set up to address the problem of water pollution and air pollution in ou country .The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) was set up in 1974 it’s main function is to investigate , collect and disseminate information related to air , water, soil pollution
iii) The Forest Conservation Act 1980 was another remarkable step in which strict provisions to control the diversion of forest land for any other purposes
GLOBAL WARMING is the nothing but increase in the average temperature of the earth atmosphere and oceans due to increase in the green house effects because of industrial revolution in developed and developing countries.
This Green House Effects is created by burning of coal and petroleum products which are the main source of carbon – di- oxide , methane, nitrous oxide and ozone.
Deforestation also causes to increase the same, Increase of methane from animal waste ,over grazing of the cattle causes deforestation also increase the global warming
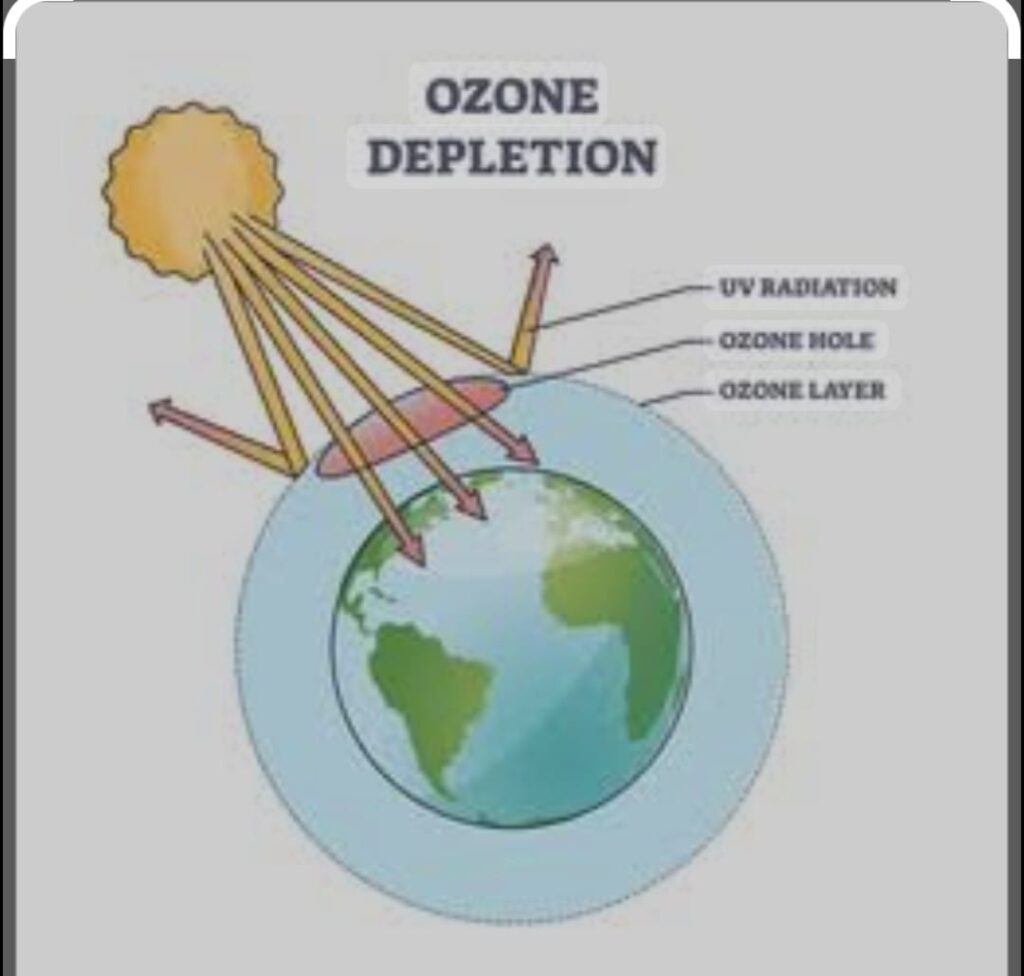
OZONE DEPLETION :
It is th in the destruction of Ozone in the Ozone layer due to presence of chlorine from the man made chloro- Floro – carbon (CFC) and many other sources.
As a result the depletion of Ozone layer more ultra – violet radiation reach the earth and causes damage to living organism of the earth .
To stop the depletion the international agreement was made in UNO as MONTERAL ACCORD which was signed by the member countries to reduce the level of CFC from the earth in the stratosphere and has helped in the ozone recovery
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT in Indian Economics part 2 is the development , which will allow all future generations to have an average quality of life at least as high which is being enjoyed by current generations
Controlling the human population to the level within the carrying capacity of the environment , technological progress should be made so that inputs must be made more efficient , renewable sources of energy should be encouraged more and more instead of non renewable .
Pollution emissions should be limited to the absorption capacity of environment.
For the sustainable development non conventional sources of energy like wind / solar energy must be encouraged ,Mini hydel plants be set up in hill aeras , use of bio compost be encouraged , less use of chemicals on food products , soil and water bodies .
Therefore the use of pesticides based plants like neem must be encouraged , eco- friendly methods must be used there should be discouragement to burning of woods, cow dung , deforestation use of LPG a and CNG as fuel for domestic and transport must be encouraged to create sustainable development in the society.
Conclusion: Indian Economics part 2
We have given the basic idea in Indian Economics Part 2 about the unemployment, it’s causes , measure and sustainable development in Indian Economics it’s causes and measure to control different kinds of pollution which is according to syllabus of class 12
Follow us on: Facebook
Read More: Indian Economics part1