Light Reflection Refraction
Light Reflection Refraction Chapter of Physics of Class 10th that Covers the Syllabus of the class gives basic idea of reflection and refraction with formation of images .

LIGHT AND IT’S PROPERTY:
Light is the form of energy which produce the sensation of sight, it travels in electromagnetic waves which requires no medium so it can travel through vacuum in Straightline, it has dual nature as wave nature as well as particle nature, it produces shadow, speed is 3×10^8 meter/sec. It experiences, interference and diffraction.
REFLECTION :
When a ray /beam of light strikes on smooth and polish surface after obeying some laws it goes back in the same medium. we can also say the bouncing back of light from the polish and smooth surface in the same medium like mirror.
LAWS OF RELECTION:
i)the angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection,
i=r
ii) The incident ray, reflected ray and normal all lie in the same fig.
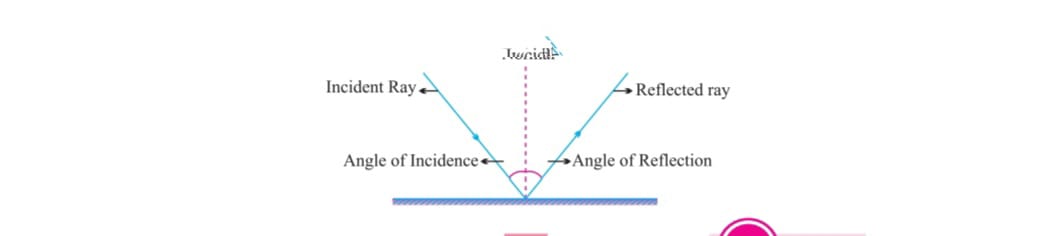
IMAGE:
when two or more rays of light actually meet or appear to be meeting it form image.
It is of two type first real image when two or more rays actual meet at a point it forms real image which can be obtained on screen, inverted images formed on cinema screen other type of image is virtual it is formed .
when two or more rays appear to meet but actually do not meet this image cannot be taken on screen it is always erect image formed on plane mirror or convex mirror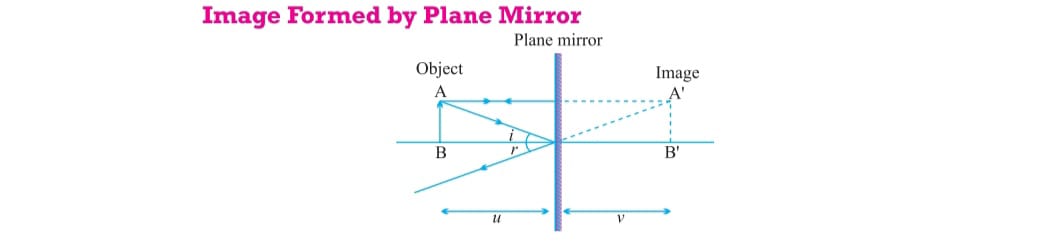
IMAGE OF PLANE MIRROR:
The image formed by plane mirror is virtual, erect, same size of the object, distance between object and mirror is same between mirror and image behind the mirror and lateral inversion (image position of left side is seen on right in the mirror and right position appear on left side in the mirror)
SPHERICAL MIRRORS:
The mirrors whose reflecting surface is curved are called spherical mirrors ,they are of two type
i) convex mirror whose reflecting surface is bulging one or outward these kinds mirror are divergent mirror in which rays spread after reflection the image formed is virtual
ii) Concave mirror whose reflecting surface is hump one or inward it is convergent mirror which allow the rays to meet at a point after reflection most of images formed are real 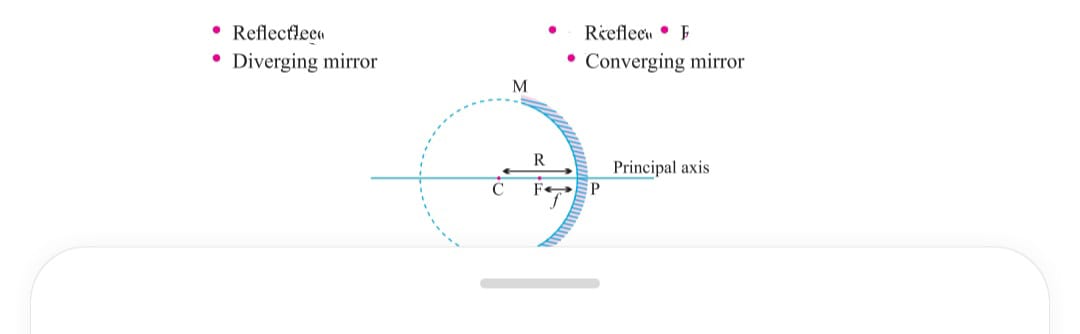 FUNDAMENTAL FACTS :
FUNDAMENTAL FACTS :
i) Principal axis is the line joining the pole and center of curvature
ii) Pole (p) it is the center of spherical mirror
iii) Aperture is the effective diameter of spherical mirror
iv) Center of curvature (C) is the center of hollow glass sphere from where mirror has been taken
v)Radius of curvature (R) is the radius of the hollow sphere from where has been taken.
vi)Focus (F) it is the point on principal axis where the parallel ray of light after reflection meet or appear to be meeting
vii) Focal length (f) it is the distance between pole and focus of the mirror
Relation f= R/2
focal length = radius of curvature /2
Magnification =height of image / height of object m = h’/h = -v/u
if m=1 size of image is equal to size of object ,
m<1 size of image is smaller than size of object
m>1 size of image is larger than size of object .
1/f = 1/v+1/u
f= focal length
v= distance of image to pole
u =distance of object to pole
SIGN CONVENTION:
Types of mirror
a) Concave Mirror U is negative, v, in case of real image positive in case of virtual positive , R is negative , height of object positive ,height of image is negative for real positive for virtual image.
b) Convex Mirror U is negative, v is positive for only real image, , height of object ,height of virtual image is positive.

RULES FOR MAKING RAY DIAGRAM BY CONCAVE AND CONVEX MIRROR.
Concave Mirror:
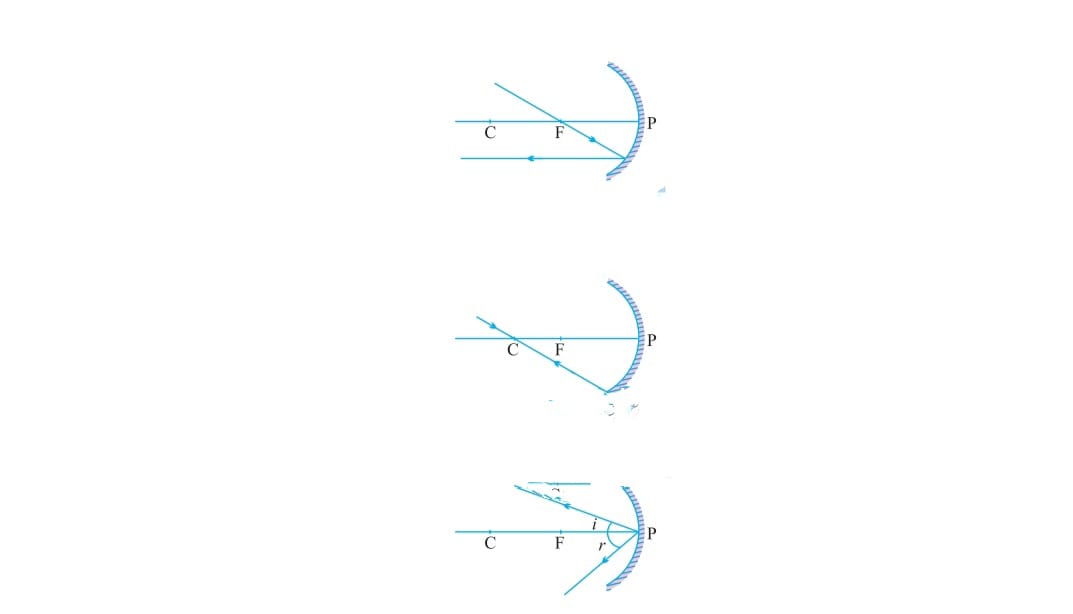
i) When a ray parallel to principal axis after reflection passes through focus
ii) A ray from focus after reflection goes parallel to principal axis
iii) A ray passes through center of curvature goes back to the same path after reflection
iv) A ray incident obliquely to the pole of principal axis of concave mirror is reflected back with same angle/equal angle.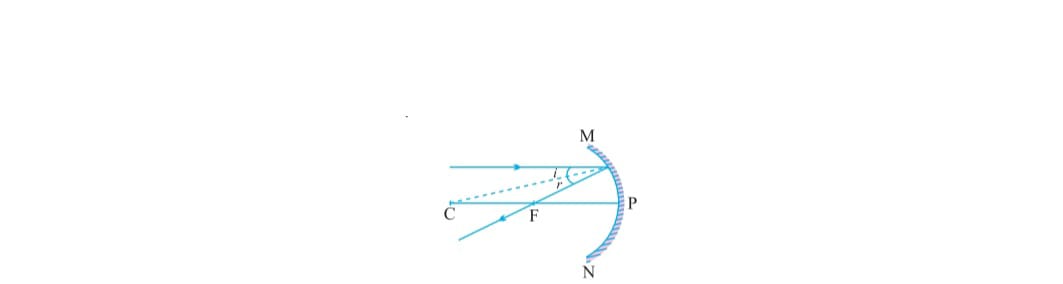
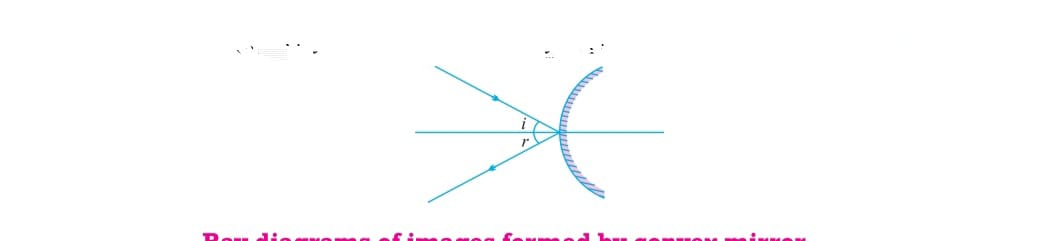
CONVEX MIRROR :
i) A ray to parallel axis after reflection appear to be passing through principal focus.
ii) A ray which is passing through the focus of mirror after reflection it goes parallel to principal axis
iii) A ray directed towards the center of curvature retraces its path .
iv) A ray incident obliquely to principal pole of principal axis of convex mirror reflected obliquely with same angle.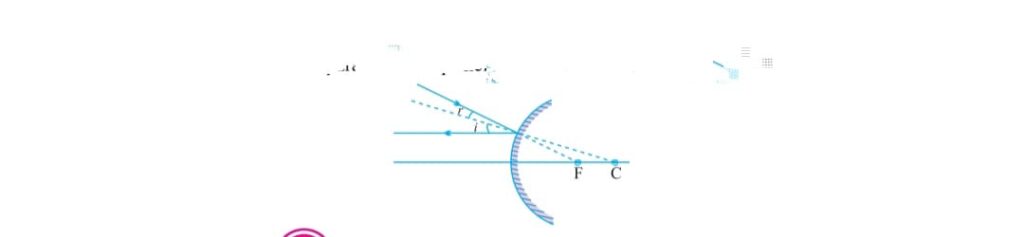
RAY DIGARAMS FOR IMAGES BY CONCAVE MIRRORS
a) when object is at infinity image formed at focus which real, inverted and diminished
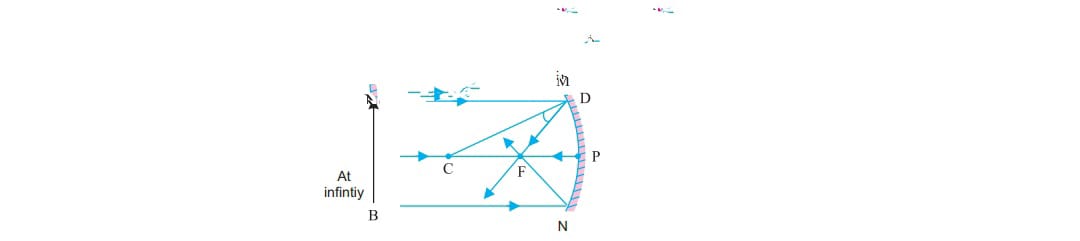
b) When an object is beyond center of curvature (C) the image formed between focus (f) and C it is real ,inverted ,smaller than object
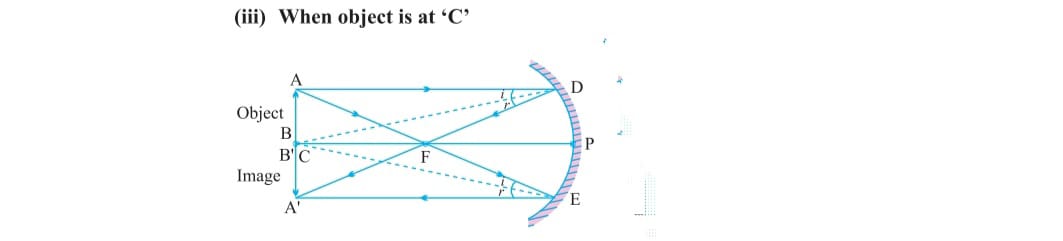
c) When object is at center of curvature (c) the image also formed at C which is real inverted and equal in size ,
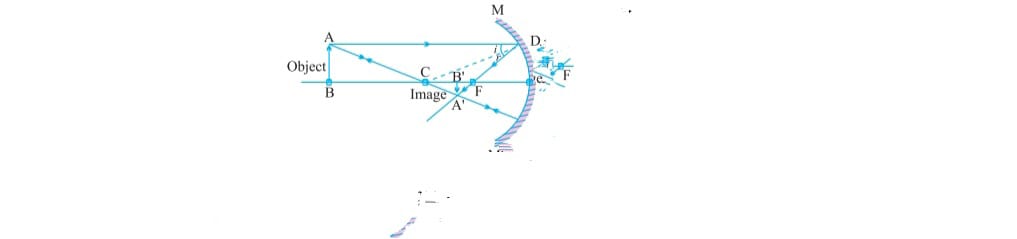
d) When object lies between focus (f) and center of curvature (C) image formed beyond C which is real inverted and bigger size than object .
e) When object is at focus image formed at infinity which is real inverted and enlarged.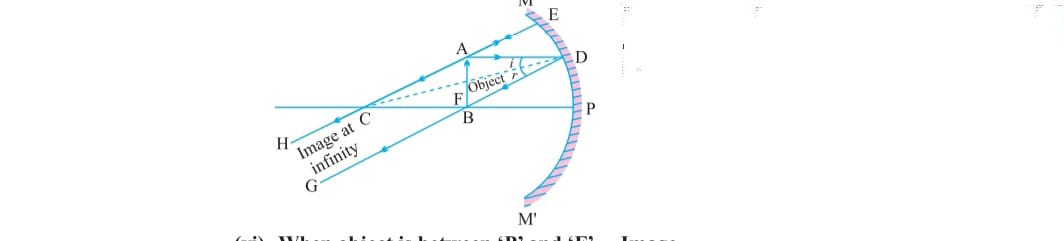
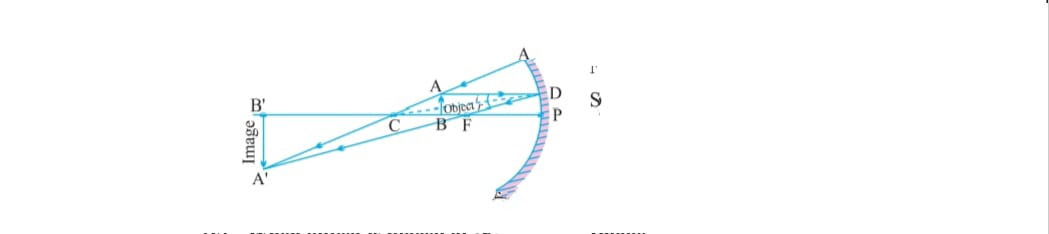
f) When object lies between focus (f) and Pole (p) the image formed behind the mirror upright/erect enlarged and virtual
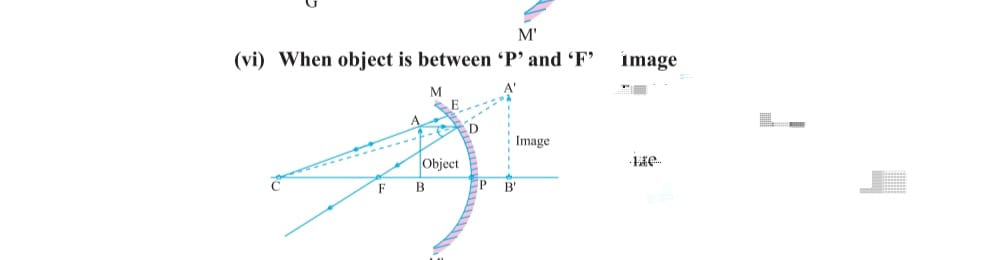
RAY DIAGRAMS OF COVEX MIRROR :
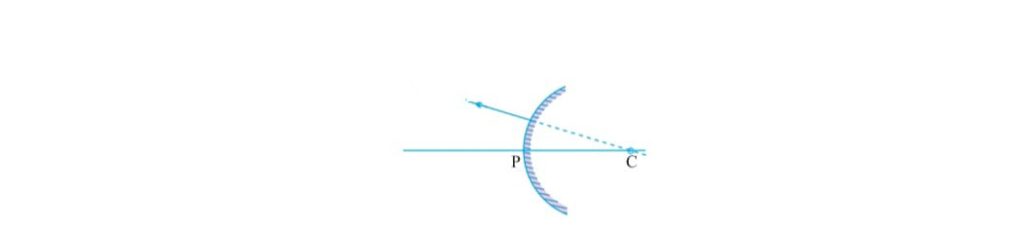
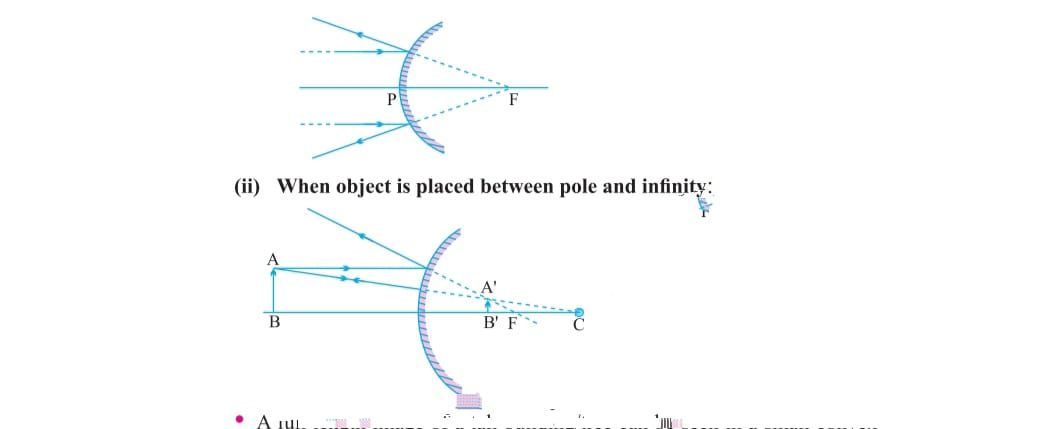
i) when object is at infinity image formed at focus ,it is virtual, erect point size.
ii) when object is placed near and in front of mirror image formed behind the mirror small virtual upright.
USES :
Concave Mirrors are used in torches, search light, vehicles headlight, it is used by dentist to see large image of teeth of patients, shaving mirror ,large mirror in solar furnace.
Convex Mirror are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles because they always give erect ,diminish image and have wider field of view, it is also used at blind turns or on the point of merging traffic ,used as security mirror.
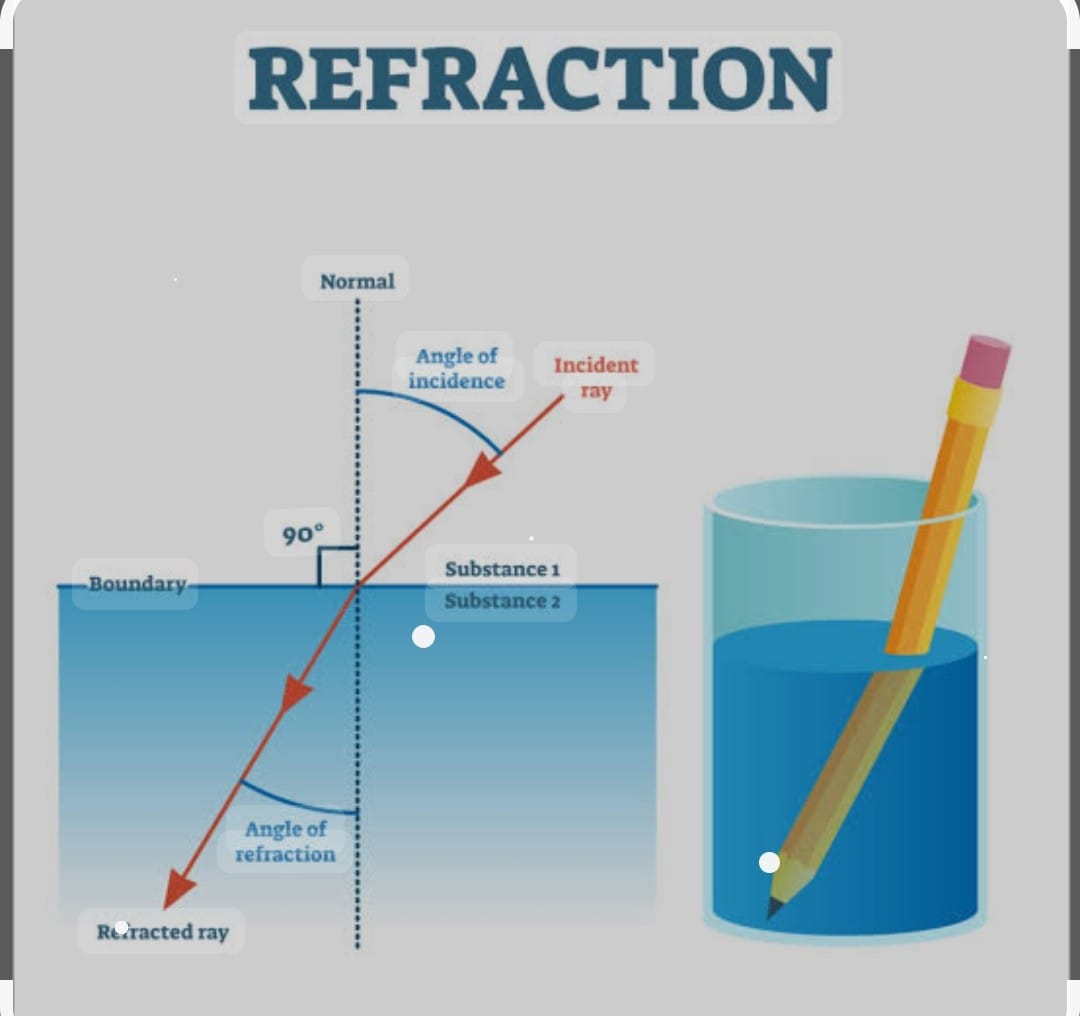
REFRACTION :
It is the process of bending of light when it passes from one medium to another .This is due to change of speed of light in different medium is different. It is maximum in air 3.10^8 m/s
some practical example as
a) Bottom of swimming pool appear higher than real depth.
b) A pencil partially immersed in water appears to be bent at interface of water and air
c) lemons placed in glass tumbler appears bigger
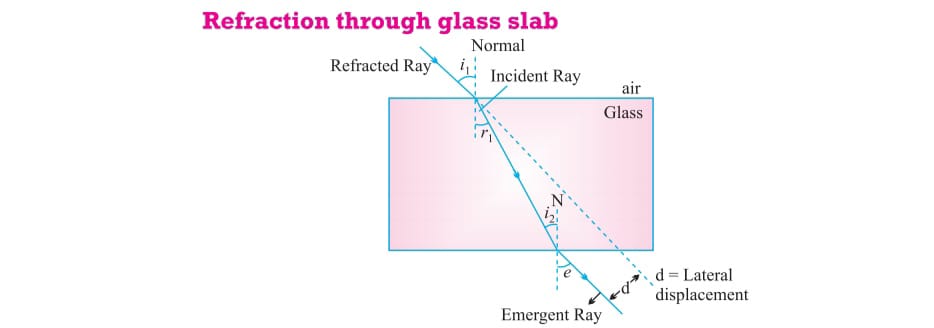
Refraction through glass slab :
When a ray of light incident on the glass slab at that point normal is drawn the angle between incident ray and normal is angle of incidence as it passes the refracted ray bends towards normal forming the angle of refraction with normal than finally the ray again comes out in form of emergent ray.
The extent of bending of ray of light at opposite face of the slab is equal and opposite. If incident ray is traced ahead the parallel distance between traced incident ray and emergent ray is called lateral displacement which depends upon refractive index and thickness of glass.
LAWS OF REFRACTION:
The incident ray, refracted ray, normal to the interface of two medium at point of incidence all lie at same plane.
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence (sine i) to the sine of angle of refraction (sine r) bears the constant ratio
It is also called Snell’s Law.
=Sine i/sine r
Refractive index = velocity of light in air / velocity of light medium
n12 =v1/v2
means refractive index of 2nd medium with respect to 1st. If we want to calculate the refractive index of 1st medium with respect to 2nd we have to calculate it’s reciprocal n21 = 1/ n12
TYPES OF MEDIUM :
There two types of medium rare and denser when ray of light passes from rare medium to denser it bends towards normal and if ray of light passes from denser to rare than it bends away from normal.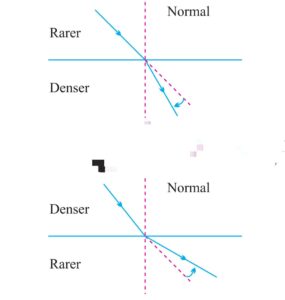
LENS :
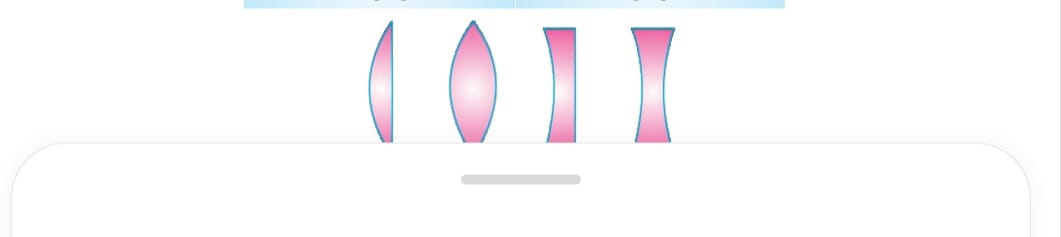
There are spherical lens which are the transparent medium bounded by two surfaces which at least one is curved It is of two kinds
a) Convex lens they are thin at edges thick at center and convergent in nature
b) Concave lens they are thick at edges and thin at center and divergent in nature.
RULES FOR IMAGE FORMATION
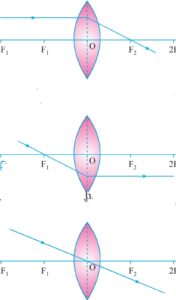
CONVEX LENS:
A ray parallel to principal axis after refraction passes through focus on the other side .Aray passing from focus after refraction goes parallel ot principal axis and if it passes through optical center it goes without any deviation.
CONCAVE LENS:
If a ray parallel to principal axis after refraction appears to be passing through focus on same side, if it is passing through focus ray appears to diverge from principal focus of same side and it passes through optical center without any deviation.
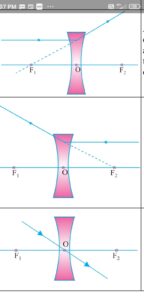
SIGN CONVENTION:
It is as in Convex and Concave
1/f = 1/v- 1/u
f is focal length for convex lens it is positive for concave it is negative;
u is the object distance from optical center negative in all cases
v image distance from optical center if to the opposite side of object, it is positive otherwise negative.
Magnification:
It is the ratio of height of image to height of object
m = height of image/height of object
m= v/u .
m =image distance / object distance from optical center.
RAY DIAGRAMS:
CONVEX LENS:
a) When an object is at infinity image formed at focus real inverted and diminished.
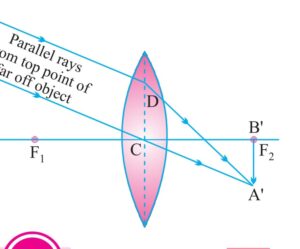
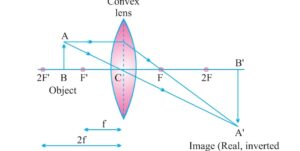
b)When object lie beyond 2f the image formed between f and 2f on the other side of lens real inverted and smaller than object
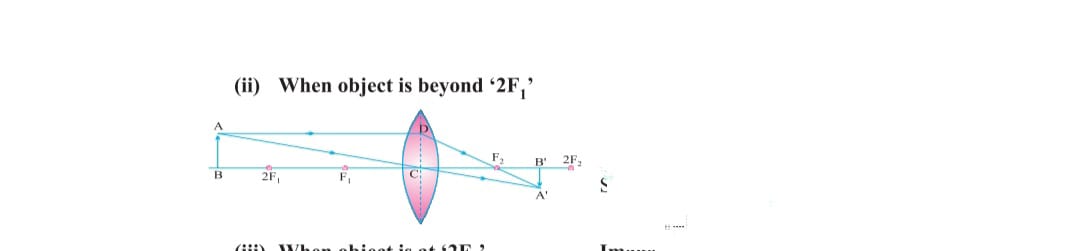
c) When object lies at 2f image is also formed at 2f image is real ,inverted equal in size .
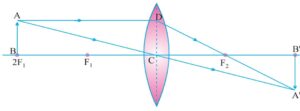
d) when object lies between f and 2f image formed beyond 2f image is real, inverted and bigger in size
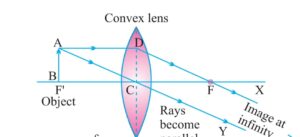
e) When object lies at f image formed at infinity real inverted and enlarge .
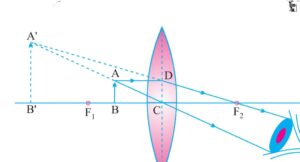
f) when object lies between f and optical center of lens image formed behind the object magnified and virtual and erect.
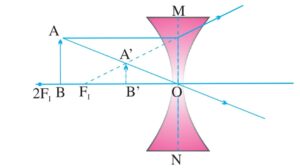
CONCAVE LENS:
a) When object is at infinity image formed at f it is virtual erect and diminished.
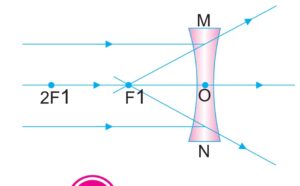
b) When object between infinity and optical center the image is formed between f and optical center towards the same side of object smaller in size ,erect and virtual.
POWER OF LENS ;
It is reciprocal of focal length taken in meters
power of lens = 1/ focal length in meters
unit of power is dioptre =D = m¯¹ for convex lens power of lens is +ive
for concave power of lens is -ive.
power of lens is inversely propo
rtional to thickness of lens
P= P1+P2+P3——.
Conclusion : Light Reflection Refraction
Light is the form of energy which help us to see objects .It has dual character as particle nature and wave nature. Reflection is the bounces back of light from smooth surface after obeying some laws which are used in mirrors whereas refraction is the phenomenon of bending of light when it passes from medium to another due to change in the speed of light is different in different medium.
Follow us on : Facebook
Read More : Human Eye
( note : figure taken NCERT BOOK )