Metals and Non Metals
Metals and Non Metals is the chapter from chemistry Covers the complete syllabus of class 10 giving basic idea about metals and non metals with different physical and chemical properties along with exception which is fruitful for public exams
In Chemistry there are about 118 elements more than 90 are metals and 22 are non-metal
- Some important metals are Sodium (Na), Potassium(K) Calcium (Ca) Magnesium (Mg)Iron (Fe)Aluminum (Al)
- There are some non-metals very common such as oxygen(O) nitrogen (N) Hydrogen (H) carbon (C) etc)
- Parts of machines, defiance, utensils, jewelry cars, trins etc are the gift of METALS.
- carbon as fuel hydrogen as fertilizers ghee, oxygen as respiration is from NON-NETALS.
- PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF METAL:
- Metals are solid at room temperature but mercury is liquid at room temperature.
- Metals are ductile (it can be drawn into wire) and malleable (can be converted into sheets) in nature
- They are sonorous (produces sound) and lustrous (shiny) in nature.
- Metals have high melting point, but cesium and gallium have low melting point.
- They are good conductor of heat and electricity but lead and mercury are not.
- They have high density, but sodium and potassium have low density.
- They form metal oxide which is basic or amphoteric. and ionic in nature.
- Some of the metal when react with dilute acid displaces hydrogen and produces hydrogen gas
- PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF NON- METAL
- Non- Metal are found in all the three states i.e., solid (Iodine) , liquid (Bromine) gas (Cholrine)
- Non-Metals are non-ductile and nonmalleable.
- They have low melting point except diamond. Non – metal is poor conductor of electricity but graphite is good conductor
- Non-Metals are acidic in nature, does not displaces hydrogen from dilute acids, they are covalent in nature.
-
chemical Properties of metals
- REACTION WITH AIR
- Metals can either be burnt or reacted
- Metal +Oxygen. ————-> Metal Oxide
- Metals like sodium (Na), Potassium(K) are very reactive with waterpower in so they are kept in kerosene oil they have vigorous rection.
- Metals like magnesium (Mg) aluminum (Al) Zinc (Zn) lead (Pb) react slowly with air forms the protective layer.
- Magnesium (Mg) can be burnt in air, combined with Oxygen to form it’s Oxide.
- Iron (Fe) and Copper (Cu) does not burn in air but combine with oxygen to form it’s oxide.
- Silver, Platinum Gold does not react with air whereas iron filings burn when sprinkled inflame.
- 4Na+ O2——>2Na2O
- 2Mg +O2——-> 2MgO
- 2Cu+ O2——–>2CuO (black)
- 3Fe +2O2——>Fe3O4
- There are some metals that react with both acids as well as base they are called Amphoteric oxides such as ZnO ,Al2O3
- Al2O3+6HCl————-.>2AlCl3+3H2
- Al2O3+ 2NaOH——–>2NaAlO2(sodium aluminate) +H2O
- Na, K, Ca reacts with cold water. 2K+ 2H2O———.>2KOH+ H2
- Ca+2H2O——–.>Ca(OH)2+H2
- Mg+2H2O———>Mg (OH)2+H2 (hot water)
- In the above two reactions for Ca and Mg the metal starts floating because bubbles of H2 gas sticks with the metal and make them float on the surface. Incase of Fe and Al both of them react with steam to give H2
- 3Fe+4H2O (g) ———>Fe3O4+4H2
- 2Al+3H2O(g)———–>Al2O3+3H2
-
Reaction with dilute acids
- Some metals react with dilute acids such as dil.HCl and dil.H2SOp4 form its salt, gives H2(g)
- Metal+ dil acid————-> Salt+ Hydrogen (g)
- Al+6HCl———–>2AlCl3+3H2
- Mg+2HCl———–>MgCl2+H2
- Zn+H2SO4———->ZnSO4+H2
- remember that copper, mercury, silver don’t react with dilute acids. Metals react with dilute Nitric reduce acids get oxidized produce H2O, but Mg and Mn are exception in this case. Mg+2HNO3————-.>Mg(NO3)2+H2 Note thatHNO3 is a strong oxidizing agent gets reduce to N2O, No, NO2.
-
Reactivity series
- It is the group of elements taken in decreasing order of reactivity. The reactivity order is K>Na>Ca>Mg>Al>Zn>Fe>Pb>H>Cu>Hg>Ag>Au It is to be noted that reactive meatal displaces low reactive metal eg Ca replaces Al, Fe or Cu salt solution but reverse not possible .Cu +2AgNO3——>Cu (NO3)2+Ag here in the reaction cu is more reactive than silver so copper displaces NO3 from Ag
-
Reaction of metals with non- metals
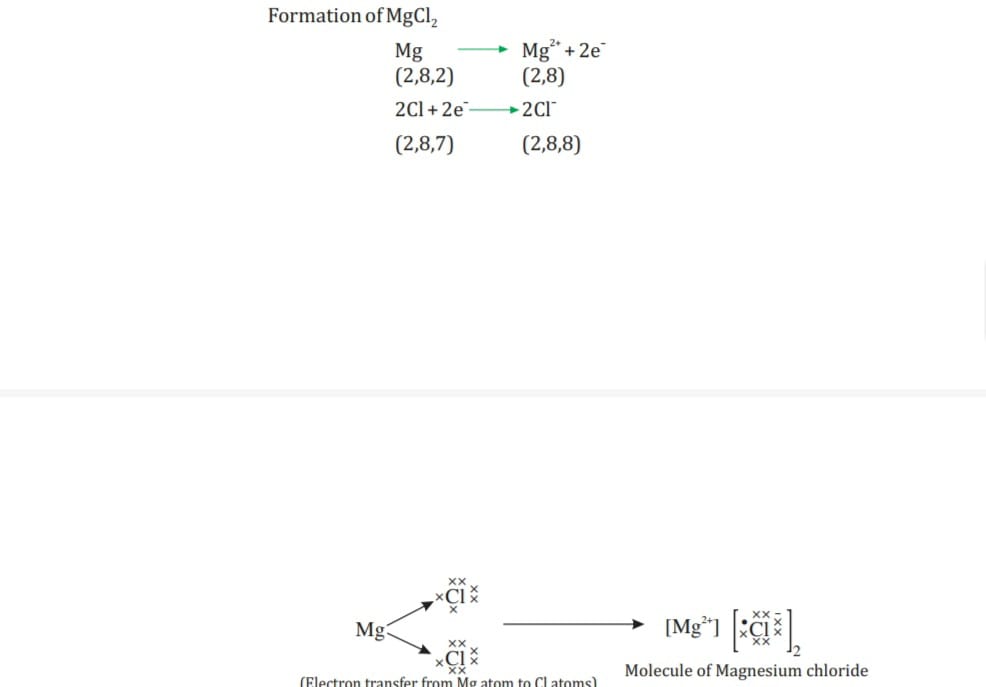
- Every element has tendency to attain the completely filled valance shell. Atom of metal loses electron becomes +ive charge ion called cations whereas atoms of non- metals accept the electron becomes -ive charge anion eg in Na electronic configuration is2,8,1 loses one electron becomes Na+ cation with react with Cl configuration 2,8,7 accepts electron form anion configuration 2,8,8 Cl- than combine to form ionic compound NaCl.
- Na+ —— Cl- ———-NaCl
-
Occurrence of metals
- The Earth Curst is the major source of metals. Sea water is also the source of salts such as NaCl ,MgCl2.
- The elements which are present in the earth curst in the natural state is called mineral.
- When the particular metal is extracted from the mineral with profit motive is called ores
- The elements in the bottom /last in reactivity series are least reactive mostly found in free state.eg gold, silver, platinum and copper. as Silver and Copper are also found in combined state Sulphide or Oxides.
- The metals such as K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al are very reactive never found in free state, The elements in the middle of reactivity are found in oxides sulphides or carbonates they are Zn, Fe, Pb.
- The ores of most of metals are found in oxides because. oxygen is found it abundant quantity on the earth curst.
- Gangue is the impurities of sand, soil present in the ore to be mined, These impurities must be removed before extraction.
- Metals in low reactivity their oxides are reduced simply by heating. In case of mercury sulphide gives mercury oxide on heating and further changes to mercury
- .2HgS(s) + 3O2 (g) ——–> 2HgO(s) + 2SO (g)
- 2HgO ——.> 2Hg +O2
- 2Cu2S+ 3O2–heat——-> 2CU2O +2SO2 2) 2Cu2O+Cu2S heated——-> 6CU +SO2
- Metals of moderate reactivity such as Zn Fe, Pb can easily be obtained from its oxides first convert them into oxides from its sulphide ores in the presence of excess of air this is roasting
- 2ZnS(s) +3O2(g)—-heated—->2ZnO (s)+2SO2 (g)
- The carbonate ores are changed into oxide when strongly heated in the absence of air this called calcination
- ZnCO3 –heated===> ZnO +CO2
- ZnO(s) +C (s)——->Zn (s) +CO(g) carbon coke is used to reduce the metal oxide to metal
- The high reactive metals such as Na , Ca , Al , are used as reducing agent because they can displace low reactive metals from their compound and these metals eg aluminum powder is used to obtain manganese such 3MnO2(s)+ 4Al(s)—–>2Al2O3(s) +Mn +heat similar is the case with iron oxide such as
- Fe2O3(s) + 2Al ——–> 2Fe (l)+Al2O3 (s) +heat
- The elements which are at top of the series cannot be obtained from its compounds by heating with carbon its oxide compounds cannot be reduced witjh carbon because these metals Na Mg Al Ca have more affinity with oxygen than carbon
- Electrolytic reduction is suitable. The chlorides of sodium, magnesium. calcium, can be obtained. Metal is obtained at cathode — -ive charge whereas Cl2 is produced at anode +ive charge.
- At cathode Na+ e- ——–> Na At anode 2Cl- ———Cl2 +2e-
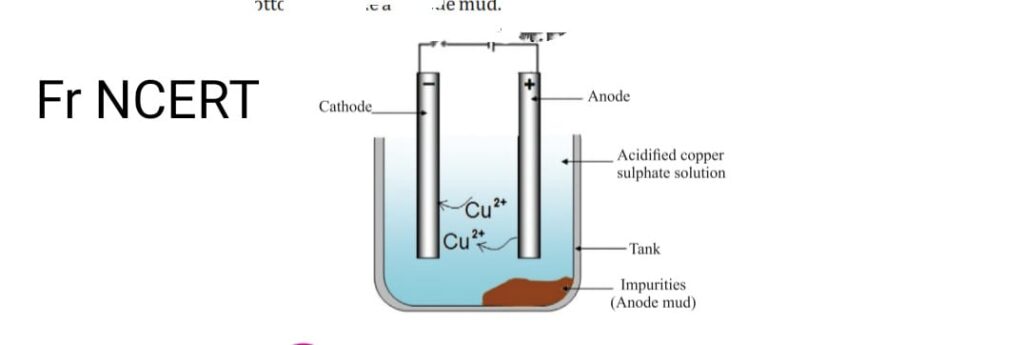
- Metals produced by various reduction methods contains lot of impurities so electrolytic refining must be done to purify them. Some metals like Cu, Zn, Ni, Ag, Au are refined electrolytically. Impure metal is taken as anode. strip of pure metal, is made cathode with the salt solution of metal. On passing the metal is current pure obtain at cathode from electrolyte soluble impurities get dissolved and undissolved settle down at the bottom as anode mud
-
Corrosion and prevention
- When metal is attacked by substance around us such as acid and moisture it is said to be corrode this is called corrosion. Silver articles become black after some time when exposed to air because it reacts with Sulphur in the air to form a coating of silver sulphide .Copper react with CO2 in air loses its shinning form the green surface of copper carbonate. Iron when exposed to moist air forms brown flaky substance called rusting.
- The rusting of Iron can be prevented.by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanize chrome plating, anodizing or making alloys.
- Galvanization is the coating of Zinc over iron to protecting iron metal.
- Making Alloying that is mixing of other metals to change the properties of metal such as stainless-steel mixture of Fe+Ni+Cr becomes hard and rust resistant. Brass is the mixture of Cu +Zn Bronze is the mixture of Cu+Sn (tin) Solder is the mixture of Pb+Sn it has low melting point and used for welding.
Anodizing of metals in this method Al is made anode graphite is made cathode O2 gas is released due to electrolysis of H2SO4 which react with Al form a thick protective layer on the surface.
Conclusion: Metals and Non Metals
Metals and Non Metals Shows different physical and Chemical Properties . Most of the Metals are shiny, malleable , ductile and good conductor of heat and electricity with the formation of basic oxide whereas non metals are dull , brittle and poor conductor of heat and electricity and form acidic oxide . Their properties are very important to understand their Industrial uses .
Read More: Chemical Reaction and Equations
Read More : Acids Bases and Salts
Follow us on : Facebook