Reproduction and Heredity Questions
Reproduction and Heredity Questions is the Science Unit of Class 10 CBSE Consist of Important Year 2018 to 2024 questions chapter wise of Organism Reproduction and Heredity Evolution .
 Reproduction and Heredity Questions
Reproduction and Heredity Questions
Read More :Life Process Important Questions
Read More : Control and Co ordination Questions
Organism Reproduction
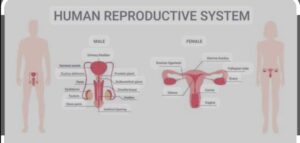
- The Cessation of menstrual cycle in human female is known as OVULATION/ MATURATION
- The reproductive life of a woman last from a) menarche to menopause b) menopause to menarche
- Lower narrow end of uterus is called ——– (urethra/ cervix)
- Other than spirogyra fermentation also occur in amoeba/Planaria.
- Which cell is formed as the product of ferritization embryo/zygote.
- i)Give an example of flowers having both stamens and carpels (Mustard ,Hibiscus or china rose) ii) What is DNA and parthenogenesis ? iii) What an example of organism having binary fission and multiple fission. ?iv) Name two examples where budding takes place ? v) Give three examples of organism having a)spore formation. b)budding
- Name three methods by which plant reproduces by stems ? What is the functions of sepals and petals ? . Give the name to scientific terms a)the mechanism by which the variation are created and inherited b)the development of new type of organism.
- Where the male gametes and female gametes of flower are produced.
- Name two STD’s. Name the causative organism of AIDS (expanded form)How can it be prevented?. Write the advantages of vegetative propagation. Name the male and female gonads where sex hormones are produced. Name the male and female gametes. Where is embryo sac present in flower? Among Jasmine, Wheat Mustard , Banana which of them reproduce by vegetative propagation?
- What happens when Vas Deferens gets blocked in male or fallopian tube in female. Name the two type of opening of female reproductive system.? What is the function of DNA where are found? what happens when a mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length? Planaria gets cut into two pieces?
- What other name is given to bisexual organism.
- What is pollination? Name the agents of cross pollination .Name the parts of stamen.
- List two methods i) male ii) female of contraceptive . Explain how organism create an exact copy of themselves.
- With the help of diagram show different stages of binary fission of amoeba.? Type of reproduction in Hydra, Planaria ,Malarial parasite ,Potato. ,earthworm ,frog ,Rhizopus ,Plasmodium
- Write the function of secretions of prostate gland and seminal vesicles in human.
- Variations are important for the survival of species overtime. .Why is DNA copying necessary during reproduction ? give main function of human testes. What are the role of sex hormones ? what is placenta and it’s role during pregnancy.
- Draw a label diagram of male reproductive and female reproductive system. Draw the diagram of anther, style and ovary in the flower ?
- How does the process of seed germination takes place in plants describe with help of figure
Reproduction and Heredity Related year 2024
- Explain with figure a) Regeneration b) Rhizopus multiply the spore formation c)multiple fission of plasmodium d) Fragmentation e)budding (2024)
- Name the methods used by human female to prevent the pregnancy and what are it’s side effects ii) what happen when human fertilization takes place and what will happen eggs do not fertilizes (2024) Explain th reproduction of spirogyra and Hydra.
- Name the substance which cannot be broken by biological means what are their harmful effect.
Reproduction and Heredity Questions
Related to
Heredity and Evolution
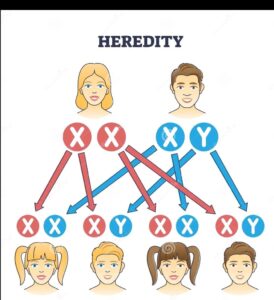
- How do the traits get expressed ?List the two difference between acquired traits and inherited traits with example.? Write difference between dominant and recessive traits.
- If the sperm bearing Y chromosome the fertilizes the egg ,the child is like his father Why it is so ?
- Why are the chances of variation more in sexually developing organism ? How can changes in genes can be brought about the change in DNA ?What are the rules of inheritance? What is sex chromosomes and autosomes ? How many chromosomes are present in human being ?
- Draw a flow chart to determine the characteristics of the progeny of a cross between tall pea plants with short pea plants with F1 and F2 generation.
- With the help pf X and Y slow the sex determination in human being.? Mention of characteristics of genes.
- The genotype of green stemmed tomato plants is denoted as GG and that of purple stemmed tomato is gg .when the crossed i)what colour of stem would you expect in F1 progeny ii) what is the percentage of purple stemmed in F2 progeny if F1 plants are self pollinated? iii) what is the ratio ?
- If a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf plant then in the first generations only tall plant appears what happens to the traits of dwarf plant? In the second generation the dwarf traits reappears why?
- Mendel selected garden pea plants for his experiments , Why? Name the dominant and recessive characters in pea plant taken by Mendel ? Name the first Indian who was aware of concept of genetics ? (Charaka was the first Indian medical practitioner who knew the factors which determine the sex of child)
- In one of the experiments with pea plants Mendal observed that when a pure tall pea plant is crossed with pure dwarf pea plant in the first generation F1only tall plants appear a) what happens to the traits of the dwarf plants in the case? When F1 generation plants are self fertilized ,he observed that a plant of second generation F2 both tall and dwarf plants are present why it happens explain .
- What is the source of hereditary information in the cell.?
- What do you mean by mutation?
- In the monohybrid cross a round seeded plant was crossed with a wrinkle seeded plant. In F2 generation genotype ratio 1:2:1 how many plants has homozygous round .?
- Exchange of genetic material takes place in sexual/asexual reproduction.
- Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red,2 pink 1 white flowers progeny than the nature of cross will be self pollination/cross fertilization.
- Human males all the chromosomes are paired except one this unpaired chromosomes may be ______–. Male is determine by _____ chromosomes and female is determined by ______–.
Two pea plants one with round green seeds(RRyy) and other with wrinkled yellow (rr YY) seeds produce F1 progeny .When F1 is crossed F2 progeny will have new combination . write F2 be combination.
Reproduction and Heredity Questions
Related to Year 2024
- i)How is the sex of a child be determined a) by what inherits from mother b) by what inherits from father c) at the time of fertilization zygote formation by male and female gametes ii) Chromosomes are a) carry hereditary information from parents for next generation b) are the thread like structure present in the nucleus of the cell c) always present in pairs in human reproductive cells d)are involved in cell division iii) Which of the following has multiple fission of asexual reproduction a) yeast b)leishmania c) Paramecium d)plasmodium (2024) iii) cross of pea plant 50%tall and 50% short that parental combination is —–—
- Important Question 2025 :If pea plants with round and green seeds (RRyy) are crossed with pea
plants having wrinkled and yellow seeds (rrYY), the seeds developed by the plants of F1 generation will be :(A) 50% round and green (B) 75% wrinkled and green (C) 100% round and yellow (D) 75% wrinkled and yellow - The correct/true statement(s) for a bisexual flower is/are :(i) They possess both stamen and pistil.(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil.(iii) They exhibit either self-pollination or cross-pollination.(iv) They cannot produce fruits on their own.
(A) (i) only (B) (iv) only(C) (i) and (iii) (D) (i) and (iv) - a) How many chromosomes are present in human beings ? Out of these how many are sex chromosomes ?
(b) Explain how, in sexually reproducing organisms, the number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained. - (i) Differentiate between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
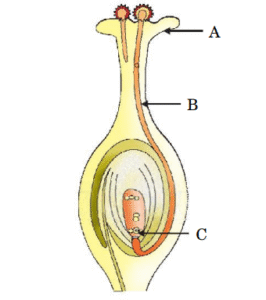 (ii) Identify A, B and C in the diagram given below and write one function of each.
(ii) Identify A, B and C in the diagram given below and write one function of each. - Bryophyllum produces new plant through :(A) Apical buds formed on the tip of the plant
(B) Vegetative buds produced in the notches of the leaf(C) Flowers produced in the notches of the branches
(D) Fruits formed on the branches of the plant - The number of chromosomes in a cell division is halved. This kind of cell division is observed in :
(A) Only testis (B) Only ovary(C) Ovary and testis both (D) All cells of the body - 8. Assertion (A) : A mango seed will germinate to form a mango tree. Reason (R) : Heredity determines the process by which traits and characteristics are reliably inherited from parents to offspring.
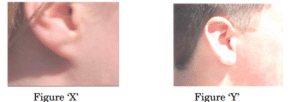
- . The lowest part of the ear called earlobe, is closely attached to the side of the head in some of us (Figure ‘X’), and not in others, called free earlobe(Figure ‘Y’). Attached and free earlobes are two variants found in human populations. The gene for free earlobe is dominant over attached earlobes. (a) A man with attached earlobes marries a woman having freeearlobes. 50% of their children have free earlobes and 50% have attached earlobes. Explain the inheritance of this trait and write the trait combinations of the progeny.
(b) Write the gene combinations of the father and the mother in the above case - When a girl is born, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs. On reaching puberty, some of these start maturing. One matured egg is released every month by one of the ovaries. The two oviducts unite into an elastic bag-like structure known as uterus.(a) Write the site of fertilization in human female. 1(b) How does the uterus prepare itself to receive and nurture the
growing embryo ? Explain. (c) (i) What happens when the egg is not fertilized ? or(c) (ii) How does the developing embryo get nutrition from the mother’s blood ? Explain. - Explain how the proteins control the ‘characteristics’ in an organism with the help of an example of ‘tallness’ trait in pea
plant.(b) Name the section of DNA that controls the ‘characteristics’ in an organism. - (a) (i) Identify the parts ‘X’ and ‘Y’ in the figure given below :(ii) Name the yellowish coloured structures produced by the
part labelled as ‘Y’.(iii) Write the name of the process by which these are transferred to the part labelled as ‘X’.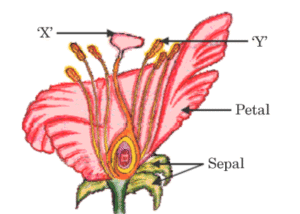 (iv) Explain the process of seed formation in a flowering plant.
(iv) Explain the process of seed formation in a flowering plant. - Name the type of asexual mode of reproduction shown in the
given figure. (ii) Identify the unicellular organism in the diagram.(iii) List any two advantages of asexual reproduction over sexual reproduction.(iv) Name and explain any one mode of asexual reproduction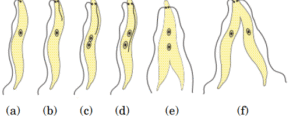 observed in Hydra.
observed in Hydra.