The Human Eye and the Colourful world
The Human eye and the colourful world is the chapter of Science Class 10 covers the complete syllabus regarding the Chapter gives basic idea of eye, it’s defect , Total Internal Reflection and applications.

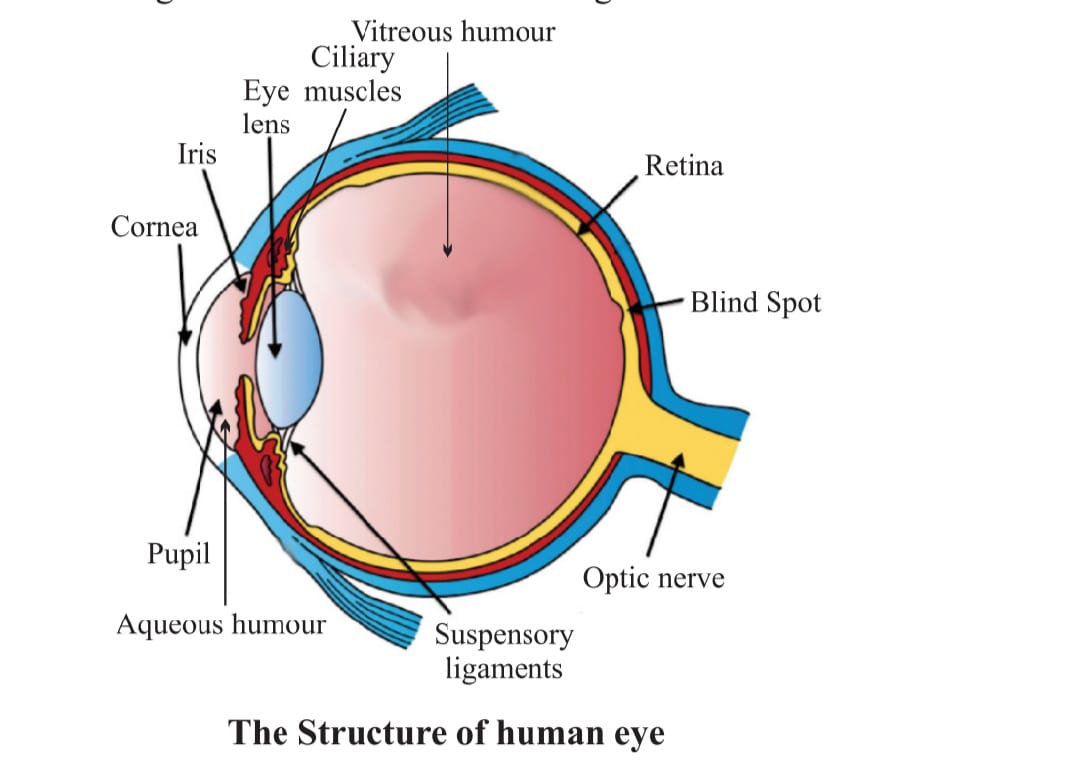
We know that eye is the sensory organ which produces the sensation of sight. It consist of following part
a)CORNEA it is a thin membrane which cover the eye
b) PUPIL it is the opening in the center of the iris to allow light to enter the eye.
c)IRIS it is the part of eye which controls the amount of light entering the eye by changing the size of the pupil.
d)RETINA it is a light sensitive screen inside the eye on which image is formed
e)OPTIC NERVE It transmit the electrical signal to brain
e) CRYSTALLINE LENS :It helps to focus light into the retina.
f)CILIARY MUSCLES : These muscles are attached to the eye lens that modify the shape of the lens which leads to the variation in focal length
.g)VITREOUS HUMOUR :It is clear gel that fill the space between the lens and retina of the eye ball it provides the shape to eye. h)AQUEOUS HUMOUR :It is the fluid inside the front part of eye between cornea and eye lens
FUNDAMENTAL FACTS :
POWER OF ACCOMMODATION is the ability of eye lens to focus near and far objects clearly on retina by adjusting it’s focal length it is limited for least distance of distinct vision is 25cm and for distance it is infinity.
PERSISTENCE OF EYE :
The sensation of the object continues in the eye for about 1/16 second in the other words it is the impression of the object seen by eye remain on retina for1/16 second even the object is removed in front of eye.
DEFECTS OF VISION
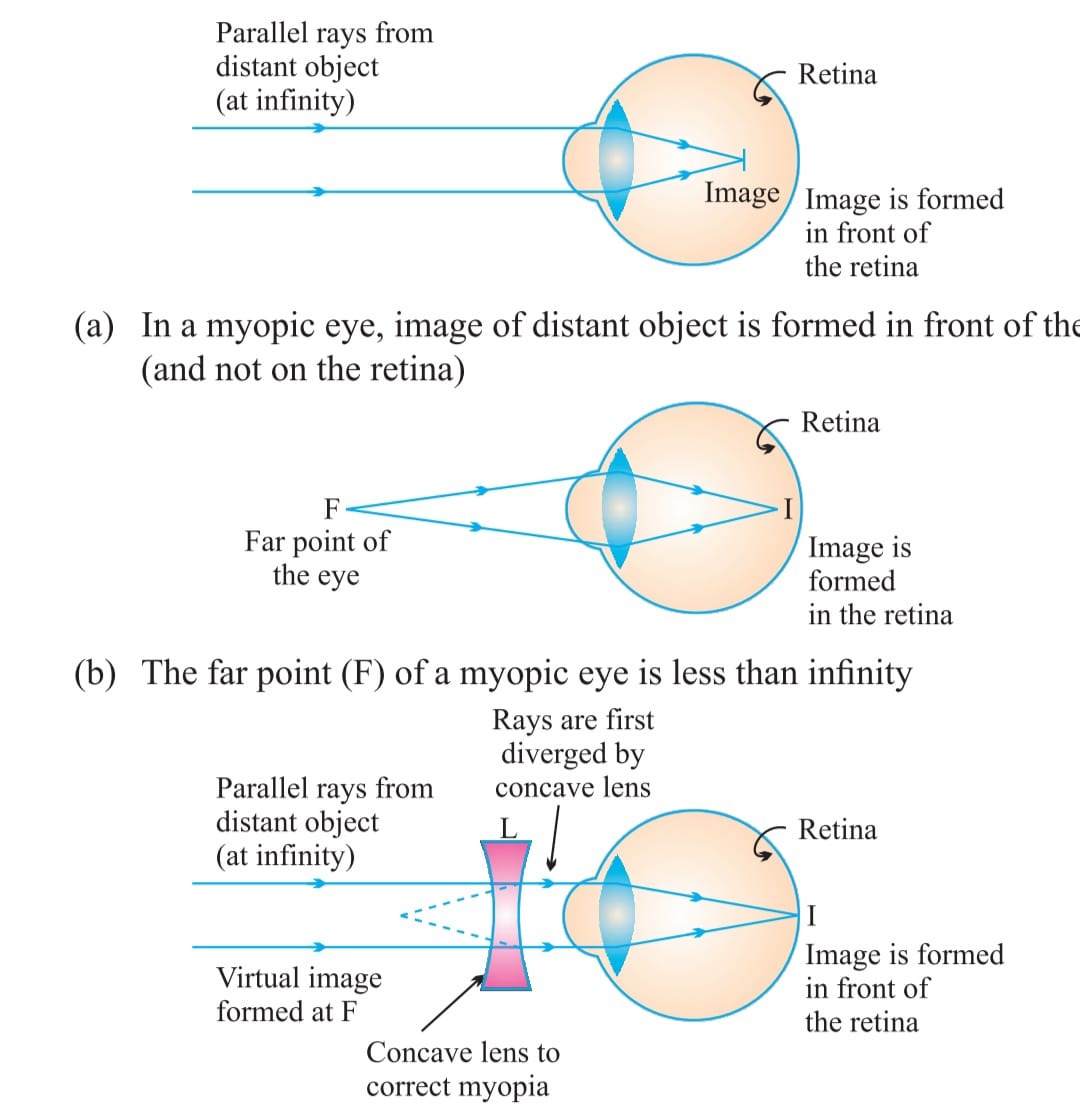
a)MYOPIA/ SHORT SIGHTNESS in this kind of defect a person can see near distance object clearly but fail to see far distance object because image formed before retina this defect is caused due to eye lens become too curved and eye ball gets elongated it can be corrected by using concave lens of suitable focal length
HYPERMETROPIA / FAR SIGHTEDNESS in this defect a person can see far distance object very clearly but unable to see near distant objects the image of the objects is formed behind the retina this defect is caused when focal length of eye lens become too long and eye lens become too small.
This defect can be corrected when convex lens of suitable focal lenght is used to form the image on retina.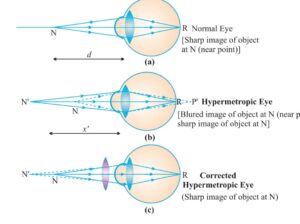
HUMAN EYE DEFECT ;
a) PRESBYOPIA in this defect the ciliary muscles gets weaken with age of a person and eye lens become rigid due to which power of accommodation of eye gets loosen this defect can be removed by using bi focal lens of suitable focal length
b) ASTIGMATISM in this defect a person cannot simultaneously cannot see both the horizontal and vertical views of the objects clearly cornea is not perfectly spherical in shape. this defect can be removed by using cylindrical lens of suitable focal length.
NEWTON was the first person who proved that white light is made of seven constituent colours he passed the sunlight through the prism to form the band of seven colours He tried to split the colours further by putting another prism ahead in inverted form but failed to get any more colours finally concluded that white light is made up of seven colours.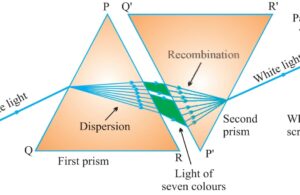
DISPERSION OF LIGHT :
When white light passes through a glass prism it splits into seven constituent colours to form the band of seven colours this is called dispersion of light
Spectrum is the band of seven colours formed due to dispersion of white light through the prism.
Acronym is a group of alphabets that represent the sequential of colours in spectrum as VIBGYOR .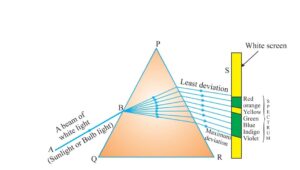
angle of deviation = 1/ wave length
red having largest wave length least deviated whereas violet having shortest wave length deviates most .
Each colour has definite wave length so angle of deviation is different for each colour therefore the spectrum is formed it is to be noted any light that form spectrum similar to sunlight is white light
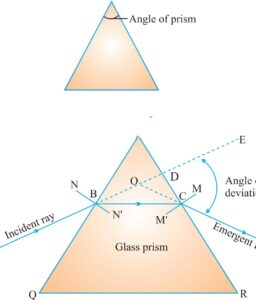
PRISM is a pyramidal piece of glass having two triangular bases three rectangular lateral surfaces the angle between two adjoining surfaces is called angle of prism
ANGLE OF DEVIATION : is the angle between incident ray and emergent ray
TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION
When a ray of light passes from denser to rare medium it bends away from normal at specific angle of incidence the angle of refraction is of 90degree to the normal making an interface to the both the medium this angle of incidence is called critical angle if angle of incidence become more than critical angle the refracted ray goes back in the same medium this is called total internal reflection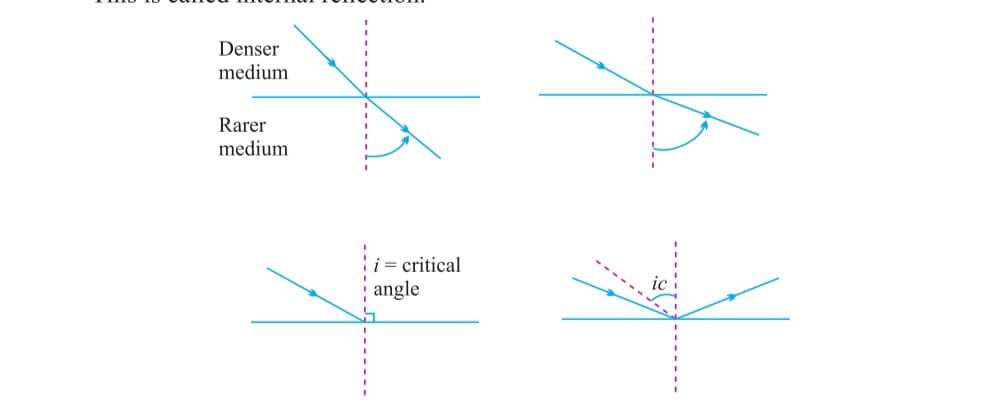
Condition for total internal reflection a) Light should obliquely from dense medium to rare medium
b) angle of incidence must be greater than critical angle.
NATURAL EXAMPLE
a) Formation of Rainbow :After rain small water droplets remain suspended in air these droplets behave like glass prism when sunlight enters the rain drops it is refracted and disperses reflect internally and refracts again when it comes out of rain drops it reaches to our eye in seven colour refractive index of hot air is less than the cool airs.
b) An object placed behind the fire appear to be flickering because air above hot surface becomes hot and rises, the space is occupied by cool air the refractive index of hot air is less than the cool air and physical condition changes regularly so refractive index also changes light comes from different direction due to which fluctuation in apparent position of objects.
c) Stars when seen near the horizon appear slightly higher than their actual position due to atmospheric refraction because the refractive index of earth atmosphere increases from top to bottom so light coming from the star near the horizon has to travel rare to denser medium bends towards the normal and appears higher.
d) Advance of sun rise /sun set : The sun appear about two minutes earlier or it continue appear two minutes later because when the sun is below horizon the rays have to pass from rare to denser medium bends away from normal appear higher from actual position
e) Stars are very far so they behave as point source of light since the physical condition of earth atmosphere changes continuously the light from the stars appear to come from different directions this create fluctuation of apparent position of star moreover the light coming from the stars also vary due to changing refractive index of atmosphere so it appear to be twinkle .
f) spreading effect of light is various direction colloid particles is called scattering effect wand when light passes through a colloid it’s path becomes visible this is called Tyndal effect scattering is inversely proportional to wavelength therefore violet ,indigo and blue scattered most and sky appear to blueish.
Conclusion : The Human Eye and the Colourful World
In “Human Eye and Colourful World”: The human eye is a remarkable organ that allows us to perceive the colorful world around us. With the help of Eye we can detect light, distinguish colors, and form images. The eye’s ability to adjust to different light conditions and focus on objects at varying distances makes it an incredibly versatile sensory organ. It helps explain many natural phenomena, such as the blue sky, colorful rainbows, and the scattering of light and also vey useful for practical applications in fields like optometry, photography, and display technologies.
Follows Us on : Facebook
Follows Us On : Instagram
Read More : Light Reflection and Refraction