Reflection Refraction and Human Eye Questions
Reflection Refraction and Human Eye Questions consist of 2 chapters Reflection and Refraction , Human Eye with application year paper questions chapter wise from 2018- 2024

Follow us : Facebook
Follow us : Instagram
Read More : Electricity and Magnetic Effects
Read More : Life Process
Read More : Chemical Reaction and Acid Bases and Salt
Reflection Refraction Human Eye Questions
Related to
Reflection and Refraction
- What is light,? what kind of wave is light ? What is real and virtual image ? For a regular reflection what is the relation between incident and reflected ray ? what is the angle of reflection when incident ray lie over normal ? What are the properties of image formed by plane mirror ?
- What the mirror formula and formula of magnification.? write the difference between concave and convex mirror ? Write two uses of each a) Concave mirror b) convex mirror.? Define the focus , center of curvature , radius of curvature of mirror ? what is the relation between radius of curvature and focus of the mirror ? Name the mirror used in solar furnace how does it work ?
- What is the minimum distance between object and real image ?
- Draw the ray diagram of mirror in following cases a) an incident ray parallel to principal axis in convex mirror . b) object placed between pole and focus of concave mirror?
- Does the speed of light changes in different medium and what is the result of this activity. What is the condition in refraction what light enter in medium but no refraction. Write the relation of refractive index and speed of light ? What do you mean the refractive index of glass is 1.5 ? what is absolute refractive index of medium? What is the value of 2U1* 1U2 U stands for refractive index ? what do you mean by refractive index of diamond is 2.5 ? What is Snell’s law
- Write a lens formula , it’s magnification . Is it possible to form real image of in concave lens and why ? what is power of lens ,signs for different lens What is the unit of power of lens ? what is principal axis and optical center.
- What is the relation between incident ray and emergent ray when passes through prism
- Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark the angle of incidence and angle of refraction ,lateral shift suffered by the ray . If the refractive index of gUa is 1.5 what is the value of aUg u= refractive index.
- What happens to image of convex lens when object is brought from infinity towards lens. b) When does convex lens form virtual erect enlarged image , c) real enlarged image. d) one portion of convex lens is covered with black paper will the lens produce the image ? e) form the image in convex lens when object lie between f and 2f . f) form the image when object in convex lens is placed beyond 2f.
- What should be the position of object when concave mirror is used for a) shaving b) torch producing parallel beam c) man standing in front of mirror produces very small real image and in what case the image of normal size .
- What is the rare medium and denser medium ?
- a) To get a real and inverted image of same size of that of object at convex lens of focal length is 20 cm draw the diagram. b) An object placed at a distance of 30cm in front of concave mirror of focal length 15cm draw the image and write the nature of image . c) An object is placed at40 cm in front of convex mirror of radius of curvature of 40 cm write the characteristics of image d)An object is placed at12cm in front of concave mirror of radius of curvature of 30 cm draw diagram and write nature of image. e)An object is placed at 30 cm from concave lens having focal length 15 cm find the nature and position of image. f) An object is placed 15 cm away from convex lens find the position and nature of image g) It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object using concave mirror where should object be place ,will the image be small, draw the diagram of the same h)It is required to get a magnified virtual image and diminished virtual image draw the figure with details. i) An object is placed at 50 cm form the virtual image at 10cm determine the lens and focal length. j) A divergent lens has focal length of 20 cm at what distance an object be placed to form the image at10cm find kind of lens used.
- State the two position in which concave mirror produces magnified image give the nature of image.
- i)The absolute refractive indices of glass 3/2 water 4/3 find the speed of light in vacuum and speed in water. ii) An image of candle is formed at 90 cm when placed at 45 cm find the type of lens and focal length. find the height of image if height is 2cm. iii)A 4cm tall object is placed in front of convex lens of focal length of24cm the oject distance is 16cm find the position , nature ,height of image. iv) A 5cm high object is placed in front of convex lens of focal length 12cm the object is placed at 8 cm find the position ,height nature of image. v) A student focused the image on white screen the position of object is 10 cm , lens position is 50 cm screen is at 90 cm find focal length ,nature of image, find the position of image if object is shifted to position of 30cm tow lens . vi) A student wants to project image at90cm screen while keeping the object at 15cm find the mirror used, linear magnification draw the diagram. An object of height
- i)At what distance from the convex lens should the object be placed to get image of same size of object ? ii) An object is placed at the distance of 10 cm in front of convex mirror with focal length of 15cm find nature and position of image (2024) iii) State two laws of refraction ? What is absolute refractive index iv) The absolute refractive index of glass is 1.5 speed of light in air is 3×10^8 m/s what the speed of light in glass .? (2024)
- If the image of an object in a mirror is real, inverted and magnification is -1 , If image formed at 30 cm from the mirror find the position of object and nature of mirror . Where would the image be if object is moved 15cm towards the mirror . ii) The upper half of Convex lens is covered 2Fwith black paper find the image when object is placed at 2F Draw the fig. state the nature, position of image . State the difference in image if lens remain uncovered. iii) Find the distance of image when an object is placed at the distance of30 cm in front of concave lens with focal length is 15 cm.(2024) iv) A object is placed at 8cm in front of concave mirror of focal length 12 cm find the postion and nature of image.
Reflection Refraction
Human Eye Questions
Related to
Human eye and colourful world
- What is Tyndall effect ? Give examples where this effect can be noticed.
- What is the colour of scattered sunlight when the size of the particles is large ? what will be the colour of sky in the absence oof atmosphere and what colour do astronauts observe in space
- On Which light sensitive screen of eye are the images formed (2024)
- Name the defect in the diagram, how is it caused methods to correct it.
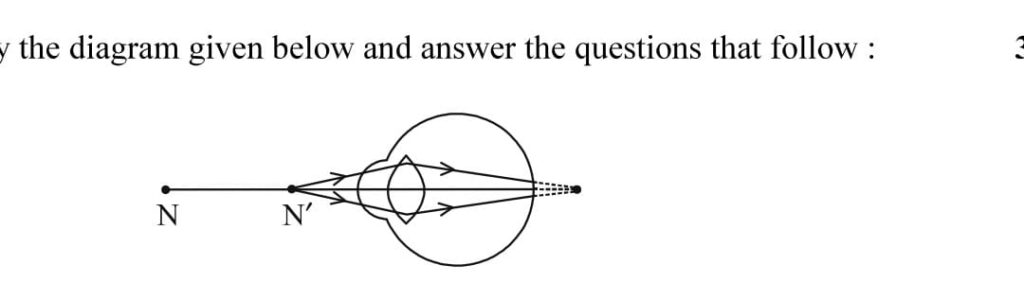
- Assertion: Myopic eyes cannot see the distance object clearly Reason : For the correction of myopia covering lens of suitable power must be used
- Important Questions 2025 :Mirror ‘X’ is used to concentrate sunlight in solar furnace and Mirror ‘Y’ is fitted on the side of the vehicle to see the traffic behind the driver. Which of the following statements are true for the two mirrors ?(i) The image formed by mirror ‘X’ is real, diminished and at its focus.(ii) The image formed by mirror ‘Y’ is virtual, diminished and erect.(iii) The image formed by mirror ‘X’ is virtual, diminished and erect.(iv) The image formed by mirror ‘Y’ is real, diminished and at its focus.
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)(C) (iii) and (iv) (D) (i) and (iv) - An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror offical length 15 cm. Use mirror formula to determine the position of the image formed by this mirror
- Draw ray diagrams to show the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex mirror when the object is placed (i) at infinity and (ii) between infinity and pole P of the mirror.
- The power of a lens ‘X’ is – 2·5 D. Name the lens and determine its focal length in cm. For which eye defect of vision will an optician prescribe this type of lens as a corrective lens
- ) ‘‘The value of magnification ‘m’ for a lens is – 2.’’ Using newCartesian Sign Convention and considering that an object is
placed at a distance of 20 cm from the optical centre of this lens, state :(I) the nature of the image formed;(II) size of the image compared to the size of the object;(III) position of the image, and(IV) sign of the height of the image - The numerical values of the focal lengths of two lenses A and B are 10 cm and 20 cm respectively. Which one of the
two will show higher degree of convergence/divergence ?Give reason to justify your answer. - (i) Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab when it falls obliquely from
air into glass.(ii) State Snell’s law of refraction of light.(iii) Differentiate between the virtual images formed by a convex
lens and a concave lens on the basis of :(I) object distance, and(II) magnification. - . If the absolute refractive indices of two media X and Y are 6/5 and 4/3 respectively, then the refractive index of Y with respect to X will be :(A)10/9(B)9/10(C)9/8 (D)8/9
- An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of a concave mirror. If its real and inverted image is formed at 60 cm in front of the mirror, the focal length of the mirror is :(A) – 15 cm (B) – 20 cm(C) + 20 cm (D) + 15 cm
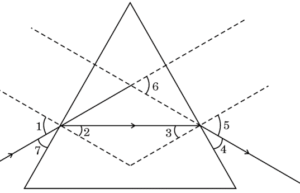
- In the given figure the angle of incidence and the angle of deviation respectively are : (A) 1 and 5 (B) 7 and 6(C) 7 and 4 (D) 1 and 6
 A ray of light after refraction from a convex lens emerges parallel to its principal axis. 2
A ray of light after refraction from a convex lens emerges parallel to its principal axis. 2
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show it.(ii) In this case, the incident ray before refraction from the lens passes through a point on its principal axis. Name the point.- Out of the two lenses, one concave and the other convex, state which one will diverge a parallel beam of light falling on it. Draw a ray diagram to show the principal focus of the lens
- A convex lens forms an 8 cm long image of a 2 cm long object which is kept at a distance of 6 cm from the optical centre of the lens. If the object and the image are on the same side of the lens, find (i) the nature
of the image, (ii) the position of the image, and (iii) the focal length of the lens. - A person allowed a narrow beam of white light from the sun to enter a dark room through a small aperture and placed a glass prism in its path in such a manner that the beam falls on the face AB of the prism as shown in the figure.A screen S is placed on the other side of the prism, facing AC. On turning the prism slowly, a beautiful band of colours is obtained on the screen. It
is the spectrum of sunlight.(a) Name the phenomenon due to which a prism splits the incident white light into a band of colours.
(b) State the reason of getting a band of seven colours in the above case. 1(c) (i) Explain with the help of a labelled ray diagram, an
experimental arrangement to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light. OR(c) (ii) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of a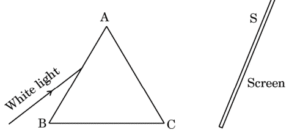 rainbow.
rainbow. - When a beam of white light passes through a region of very fine dust particles, the colour of light that scatters the most in that region is :(A) red (B) orange(C) blue (D) yellow
- A student has difficulty in reading his textbooks but can read the blackboard clearly while sitting in the last row. Name the defect of
vision the student is suffering from. List two reasons due to which this defect arises. Write the nature of the lenses required to correct this defect. - Draw a ray diagram to show the path of a ray of light falling obliquely on one of the refracting faces of a triangular glass prism
and mark the angle of deviation on it. - (i) ‘‘In refraction of light through a rectangular glass slab, the emergent ray is always parallel to the direction of the
incident ray.’’ Why ? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.What happens when a ray of light falls normally on one of
the faces of a rectangular glass prism ? Draw diagram.
(ii) An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre of a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. Use Lens
formula to determine the position of the image formed in this case. - (i) A student wishes to study the image formation by a concave mirror using candle flame as object. State the type of the
image formed by the mirror and mention the change in the image formed, if any, that he observes when the candle
flame is gradually moved away from the pole of the mirror.Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation when the
object distance is nearly equal to the radius of curvature of the mirror.
(ii) A convex mirror used for rear-view on an automobile has a focal length of 3∙0 m. If a bus is located at 6∙0 m from this
mirror, use mirror formula to find the position of the image of the bus as seen in the mirror.